Figure 3.
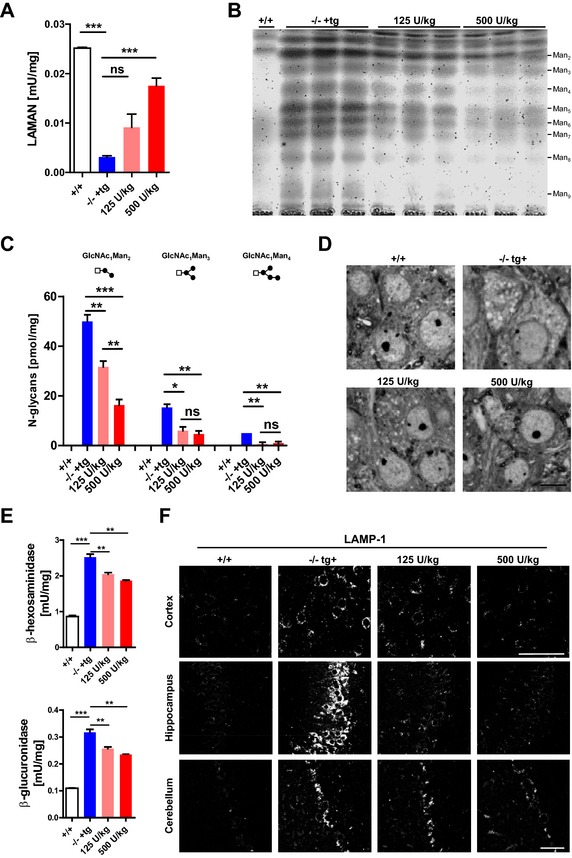
Long‐term high‐dose ERT efficiently reduces oligosaccharide storage within brain. (A) Alpha‐mannosidase activity increases dose‐dependently in brain homogenates of transgenic (‐/‐ +tg) mice after biweekly injections of 125 or 500 U/kg over 12 weeks of treatment. (B) TLC analysis of oligosaccharide brain extracts of wild‐type (+/+) and both knockout strains shows decreased levels of all major oligosaccharide species in ‐/‐ +tg mice after ERT with both indicated doses. (C) HPLC‐based quantification reveals a significant dose‐dependent decrease of Man2 and Man3 in treated ‐/‐ tg+ mice when compared to mock treated animals. (D) Toluidine blue‐stained semithin sections display less storage vacuoles in high dose (500 U/kg) treated ‐/‐ +tg mice when compared to non‐ and 125 U/kg treated mice. (E) ERT leads to a significant dose‐dependent decrease of lysosomal enzyme activities such as β‐hexosaminidase and α‐galactosidase and (F) a normalization of LAMP‐1 immunoreactivity in cerebral cortex (upper panel) and hippocampus (middle panel) but not in Purkinje cells of the cerebellum (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). ERT, enzyme replacement therapy; TLC, thin layer chromatography; HPLC, high‐performance liquid chromatography; LAMP‐1, Lysosome‐associated membrane glycoprotein 1.
