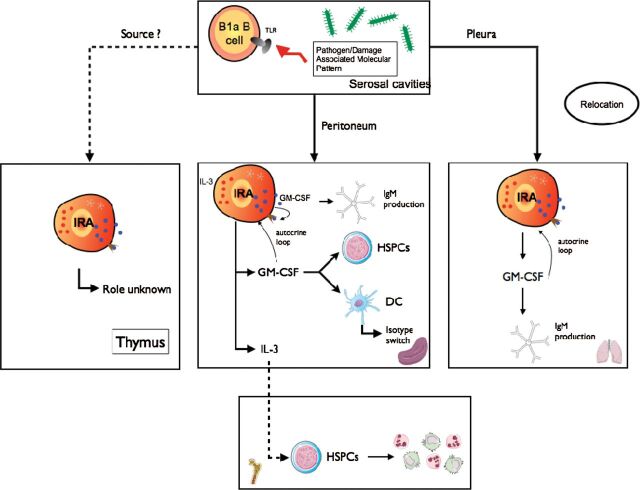
Fig. 1.
The origin and function of IRA B cells. B1a B cells, following LPS–TLR4 interaction, relocate from the peritoneum or the pleural space to spleen or lung and develop into IRA B cells. IRA B cells produce GM-CSF that enhances IgM secretion, via an autocrine loop, activate DCs and boost proliferation of HSPCs. IRA B cells also produce IL-3 which promotes neutrophil and monocyte production.