Figure 2.
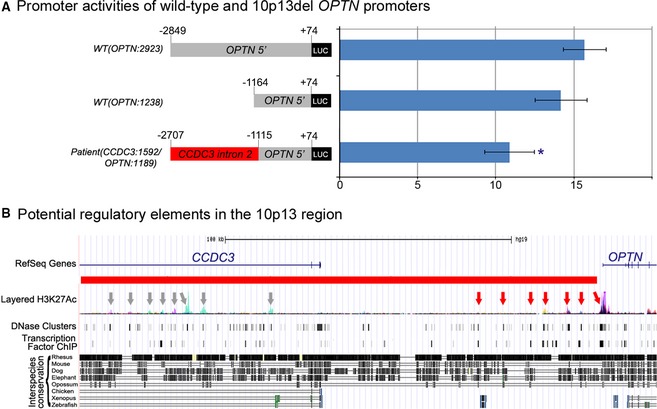
Analysis of the effect of the deletion on the OPTN promoter. (A) Promoter activities of WT(OPTN:2923)luc,WT(OPTN:1238)luc, and Patient(CCDC3:1592/OPTN:1189)luc reporters. Student paired t‐test with a one‐tailed distribution was utilized to compare values. The promoter activity of Patient(CCDC3:1592/OPTN:1189)luc demonstrated a significant decrease (marked with asterisk [*]) in comparison to experiments performed with wild‐type WT(OPTN:2923)luc reporter (P < 0.001) or wild‐type WT(OPTN:1238)luc reporter (P < 0.013). Sequences corresponding to the OPTN and CCDC3 genes are marked, with coordinates indicated in respect to the OPTN transcriptional start site. (B) Schematic of genomic region encompassing the deletion with potential distant regulatory elements indicated. Genome Browser view is shown with ENCODE project data for H3K27Ac marks (that are frequently located near active regulatory elements) on seven cells lines, digital DNase I hypersensitivity clusters in 125 cell types, transcription factor ChIP‐seq data and multiple interspecies sequence alignments highlighting regions of strong homology (often associated with conserved regulatory elements). Arrows indicate potential regulatory elements as proposed by several of the above mentioned assays; red arrows point to elements located in the intergenic space closer to the OPTN gene while gray arrows mark indicates elements positioned within the CCDC3 gene.
