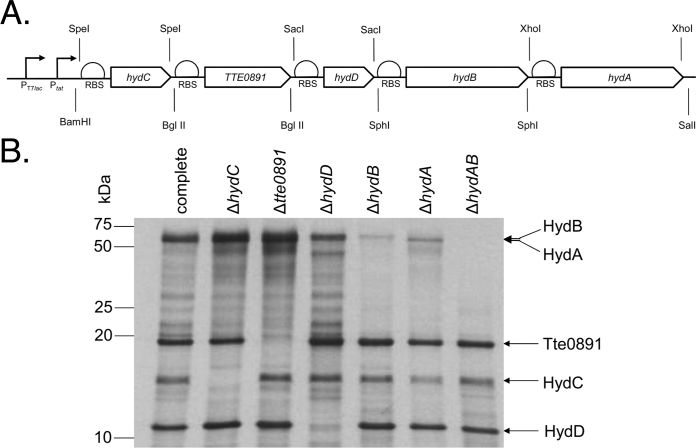
Fig. 1.
The products of a synthetic operon encoding an [FeFe]-hydrogenase are synthesised in E. coli. (A) The predicted structure of the synthetic operon encoding Ca. subterranus NADH-dependent [FeFe]-hydrogenase. Restriction sites and promoter regions are indicated. (B) The E. coli strain K38/pGP1-2 was transformed with plasmids: pUNI-Tte-Hyd (‘complete’); pUNI-Tte-HydΔC (‘ΔhydC’); pUNI-Tte-HydΔ0891 (‘Δtte0891’); pUNI-Tte-HydΔD (‘ΔhydD’); pUNI-Tte-HydΔB (‘ΔhydB’); pUNI-Tte-HydΔA (‘ΔhydA’); and pUNI-Tte-HydΔAB (‘ΔhydAB’), grown in M9 minimal medium lacking cysteine and methionine, and labelled by the addition of 35S-methionine. Protein samples were then separated by SDS–PAGE (12% w/v polyacrylamide), fixed, and visualised by autoradiography.