Figure 8.
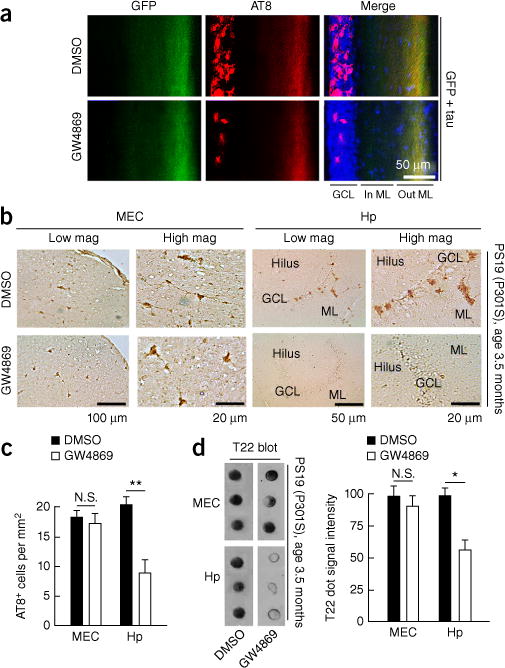
Inhibition of nSMase2 suppresses tau propagation in the DG of AAV-GFP/tau-injected and PS19 tau mice. (a) C57BL/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP/tau into the MEC and injected daily intraperitoneally (i.p.) with GW4869 or control vehicle for 4 weeks after AAV injection. Immunofluorescence image shows GFP (green), AT8 (red) and DAPI (blue) and quantification of AT8+ cells in the GCL of the DG in AAV-GFP/tau injected mice. GCL, granule cell layer; In ML, inner molecular layer; Out ML, outer molecular layer. (b,c) PS19 mice at 3.5 months of age were treated with daily i.p. injection of GW4869 (1.25 mg per kg per day in 200 μl of 5% DMSO) or control vehicle for 4 weeks and sacrificed for immunofluorescence with AT8 and quantification of AT8+ cells in the EC and the GCL of the DG in PS19 mice. N.S., no significance (P = 0.8067), t(19) = 0.2481 between DMSO (n = 3 mice, 11 sections) and GW4869-treated groups (n = 3 mice, 10 sections) in the MEC; **P = 0.0013, t(22) = 3.698 between DMSO (n = 3 mice, 12 sections) and GW4869-treated groups (n = 3 mice, 12 sections), as determined by unpaired Student’s t-test. Hp, hippocampus. Error bars represent s.e.m. (d) T22 dot blot of brain tissue lysate of the EC and DG from PS19 mice. N.S., no significance (P = 0.7512), t(4) = 0.3397; *P = 0.0136, t(4) = 4.228, as determined by unpaired Student’s t-test for each brain region (n = 3 mice per group). Error bars in d represent s.e.m.
