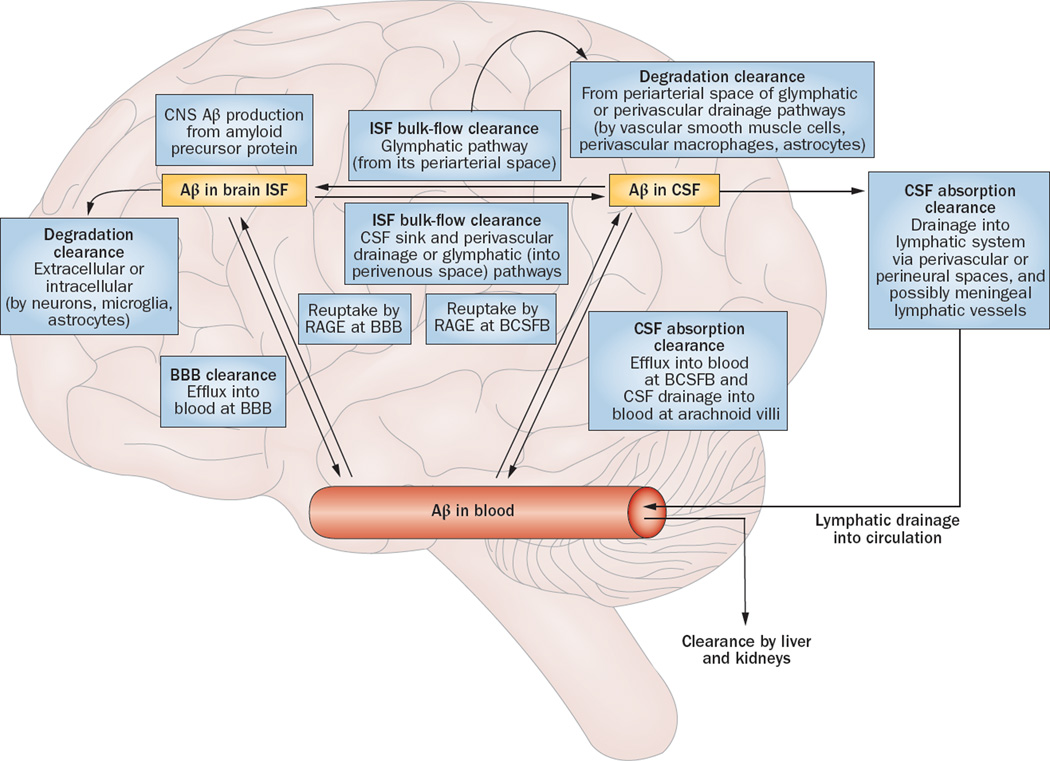
Figure 2.
Aβ clearance systems. Soluble Aβ can be removed from the brain by various clearance systems. Degradation clearance via extracellular and intracellular degradation pathways can involve either cellular uptake from the interstitium by neurons, microglia, and astrocytes, or uptake from the perivascular space by smooth muscle cells, perivascular macrophages, and astrocytes. BBB clearance involves Aβ efflux into the blood. ISF bulk flow clearance can occur into the CSF sink (ventricles and subarachnoid space), via perivascular drainage pathway, or via glymphatic pathway. CSF absorption clearance involves absorption either into the circulatory system from the arachnoid villi and BCSFB, or into the lymphatic system from the perivascular and perineural spaces—and possibly through meningeal lymphatic vessels. Abbreviations: Aβ, amyloid-β; BBB, blood–brain barrier; BCSFB, blood–CSF barrier; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; ISF, interstitial fluid; RAGE, advanced glycosylation end productspecific receptor. Adapted with permission from Nature Publishing Group © Erickson, M. A. & Banks, W. A. J. Cerebr. Blood Flow & Metabol. 33, 1500–1513 (2013).