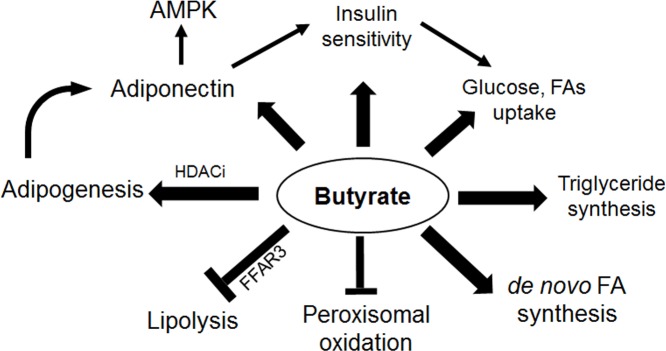
Fig 14. Schematic summary of the effects of butyrate on adipogenesis and lipid metabolism.
Lines with arrowhead represent upregulation of activity, protein content, and/or expression. Lines without arrowhead denote inhibition. Butyrate supplementation leads to induction of adipogenesis, which results in increased adiponectin secretion. Adiponectin activates the AKT pathway, thereby increasing insulin sensitivity. Adiponectin also leads to activation of AMPK. Butyrate increases intracellular triglyceride accumulation through inhibition of lipolysis and enhancement of triglyceride synthesis. Butyrate also inhibits peroxisomal fatty acid oxidation, leading to accumulation of LCFAs, which may also account for feedback inhibition of de novo fatty acid synthesis through increased ACC phosphorylation.