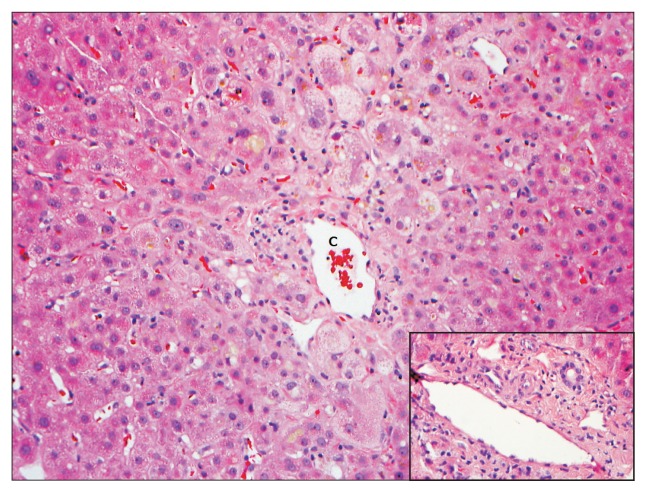
Fig. 2.
A liver biopsy from a 69-year-old male patient with a cholestatic pattern of liver injury following administration of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. The hepatic lobules showed predominantly centrizonal hepatocanalicular cholestasis and marked swelling of the perivenular hepatocytes. In this case, there was no evidence of ongoing significant biliary epithelial injury in the portal tracts (inset). The antibiotic had been held for several weeks. A biopsy was conducted for persistent jaundice and pruritus. Eventually, the patient had a full recovery (H&E stain, ×200).
C, central vein.