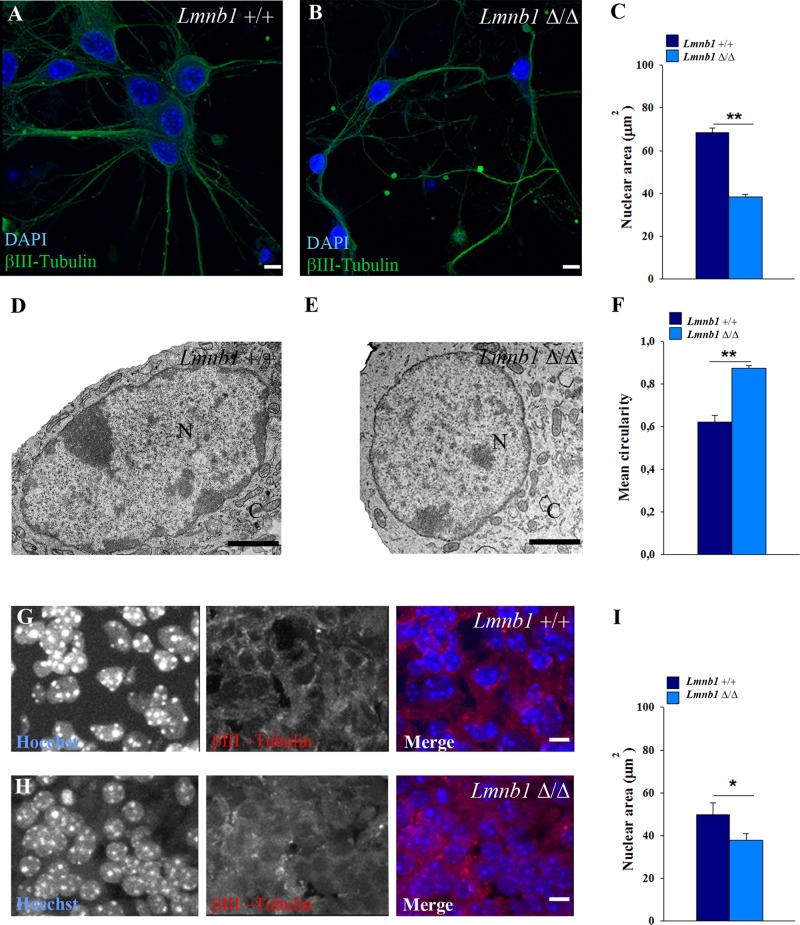
FIGURE 5:
Lmnb1 deficiency induces nuclear abnormalities in primary mouse cortical neurons. Nuclei morphology was analyzed in 7 DIV primary cortical neurons or E17.5 embryonic brain from Lmnb1+/+ and Lmnb1Δ/Δ mice as described in Materials and Methods. (A, B) Representative maximal projections of z-stack confocal images of Lmnb1+/+ (A) and Lmnb1Δ/Δ (B) neurons immunostained for βIII-tubulin. Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 5 μm. (C) Quantitative analysis of nuclear area. Bars represent the mean area ± SEM of at least 100 neurons/group. (D, E) Representative TEM images of nuclei from Lmnb1+/+ (D) and Lmnb1Δ/Δ (E) primary cortical neurons. Scale bars, 2 μm. (F) Circularity of nuclei determined using TEM images. Lmnb1+/+, n = 28; Lmnb1Δ/Δ, n = 39. (G, H) Representative maximal projections of confocal z-stack images of βIII-tubulin (red) immunoreactivity in the cortical plate of E17.5 Lmnb1+/+ (G) and Lmnb1Δ/Δ (H) embryos. (I) Quantitative analysis of nuclear area. Bars represent the mean area ± SEM. At least 100 neurons from three different embryos/genotype were analyzed. In all graphs, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, Student’s t test.