Figure 1. Alteration of the enzymatic activities of human IRE1α by site-directed mutagenesis.
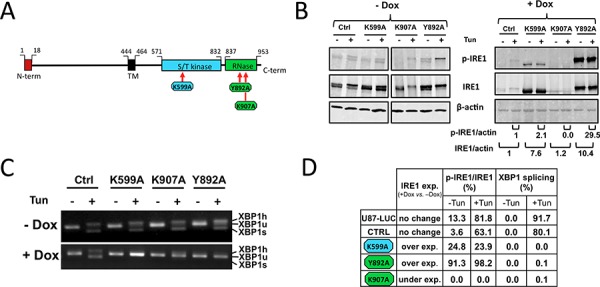
IRE1α punctual mutants (K599A, K907A and Y892A) were expressed in U87-LUC cells under the dependence of doxycycline. A. Domain organization of hIRE1α protein. Point mutations were designed either at the ATP-binding site within the kinase domain (K599A) or in the IRE1α RNase domain (K907A and Y892A). B. Measure of IRE1α autophosphorylation. Cells were incubated for 48 h with (+Dox) or without (−Dox) 2 μg/ml doxycycline and were then stimulated or not with the ER stress inducer tunicamycin (Tun) for 2 h. Whole cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-IRE1 protein antibodies. IRE1α was revealed by immunoblotting using either antibodies against phospho-(Ser724)-IRE1α (p-IRE1) or against total IRE1α (IRE1). β-actin was used as internal control. Pixel intensities of IRE1α proteins normalized to actin, and ratios of phosphorylated Ser-724 IRE1α (p-IRE1) to total IRE1α are indicated. C. Inhibition of XBP1 splicing. Cells grown with or without doxycycline were stimulated or not with tunicamycin. XBP1 transcripts were detected by PCR after reverse trancription using primers flanking the mRNA splicing sites: XBP1u, unspliced mRNA doublet; XBP1s, spliced doublet; XBP1 h, unspliced/spliced hybrid. D. IRE1 expression and relative kinase and RNase activities. IRE1 kinase activity was reported in percent of p-IRE1α to total IRE1α. RNase activity was given in percent of total XBP1 splicing.
