Figure 6. Status of PP2A activity, AKT and ERK phosphorylation and PP2A subunit associations in primary hemangioma endothelial cells.
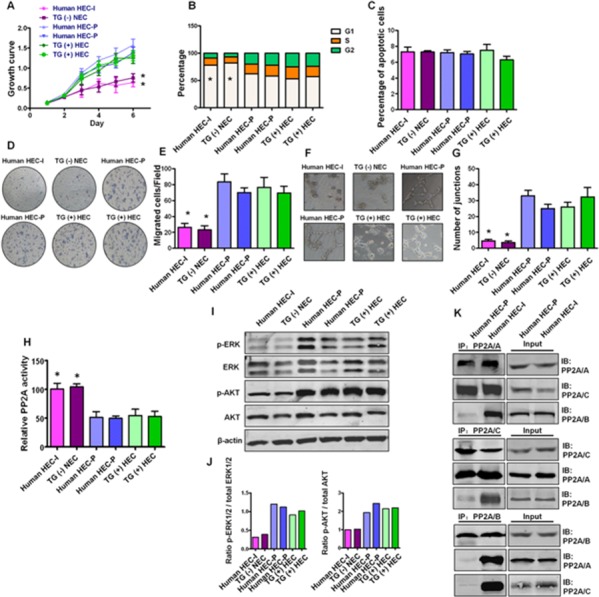
A. Growth curve shows human HEC-P cells (two lines) and TG(+) HEC cells (two lines) displayed higher proliferation ability than that of human HEC-I cells and TG(−) HEC cells. (n = 3/group, one-way ANOVA) *P < 0.05 B. Obvious G1 cell arrest was observed in human HEC-I cells and TG(−) HEC cells. (n = 3/group, one-way ANOVA) *P < 0.05 C. No significant difference in the number of apoptotic cells was observed during these cells. D. Transwell assays indicated that human HEC-P cells and TG(+) HEC cells displayed higher migration ability than that of human HEC-I cells and TG(−) HEC cells. G. Quantitative analysis of cell migration. (n = 3/group, one-way ANOVA) *P < 0.05 H. In vitro angiogenesis tube formation assay showed that human HEC-P cells and TG(+) HEC cells exhibited higher angiogenic ability than that of human HEC-I cells and TG(−) HEC cells. I. Quantitative analysis of junctions number in angiogenesis tube formation assay. (n = 3/group, one-way ANOVA) *P < 0.05 H. Phosphatase activity assay results showed that inactivation of PP2A was observed in human HEC-P cell lines and TG(+) HEC cell lines compared with human HEC-I cells and TG(−) NEC cells. (n = 3/group, one-way ANOVA) *P < 0.05 I. Western blotting results showed high levels of phosphorylated AKT and ERK in indicated cell lines. J. Quantitative analysis of the phosphorylation status of AKT and ERK. K. Immunoprecipitation and immunoblot results indicated the dissociation of the PP2A/B subunit from the PP2A AC core in human HEC-P cells, but not in human HEC-I cells.
