Figure 6. Effect of HDAC2 inhibition on IR-induced cell death.
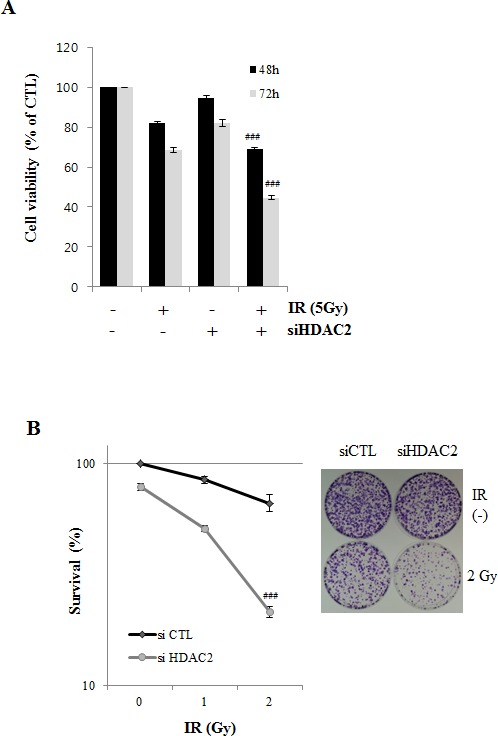
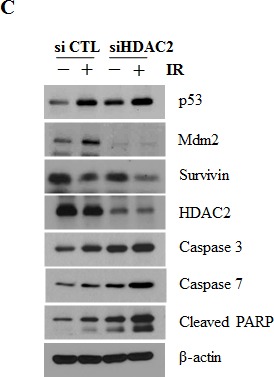
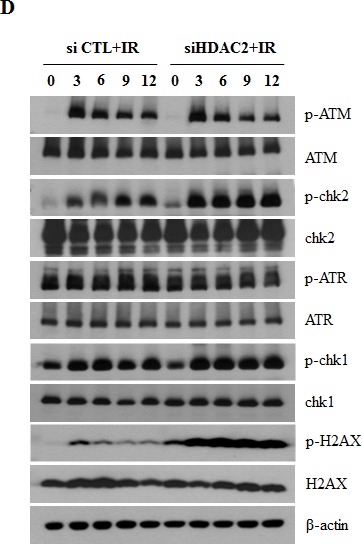
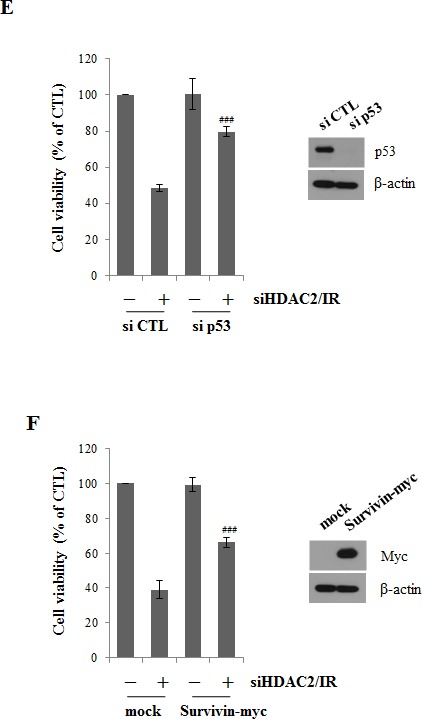
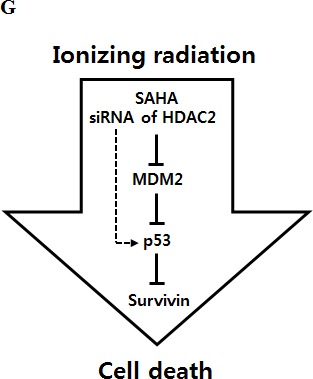
After incubation, cells were analyzed by MTT, Western blotting and colony forming assay as described in Materials and Methods. β-actin was used as a control for equal protein loading. Values were represented as means ± SD of three independent experiments. Immunoblots are representative of at least three independent experiments. A. A549 cells were transfected with 60 nM HDAC2 siRNA and then treated with IR (5 Gy) for 48 h or 72h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay, as described in Materials and Methods, and expressed relative to that of controls (defined as 100%). B. A549 cells were treated with 60 nM HDAC2 siRNA, alone or combination with IR (1 or 2 Gy). After 18 d, colonies were stained and counted. The relative surviving fractions were calculated by dividing the number of colonies in treated cells by that in controls. Each value represents the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments (###P < 0.001 vs. IR 2Gy-treated groups). C. A549 cells were treated as described for Figure 6A (48h). D. A549 cells were transfected with 60 nM HDAC2 siRNA. After 6h, then cells were treated with IR. Cells were harvested in time course. E. A549 cells were transfected with 50 nM p53 siRNA and 60 nM HDAC2 siRNA, alone or in combination, and then treated with IR (5Gy) for 72 h. Each value represents the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments (###P < 0.001 vs. si CTL/siHDAC2/IR-treated groups). F. A549 cells were co-transfected 0.2 μg survivin-myc plasmid (Survivin-myc) or empty vector (mock) and 60 nM HDAC2 siRNA and then treated with 5Gy IR for 72 h. Each value represents the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments (###P < 0.001 vs mock/siHDAC2/IR-treated groups). G. A scheme shows that SAHA or HDAC2 siRNA decreased survivin level through p53-Mdm2 pathway in A549 cells. Downregulated survivin by SAHA or HDAC2 siRNA confers enhanced responsiveness of the cells to ionizing radiation.
