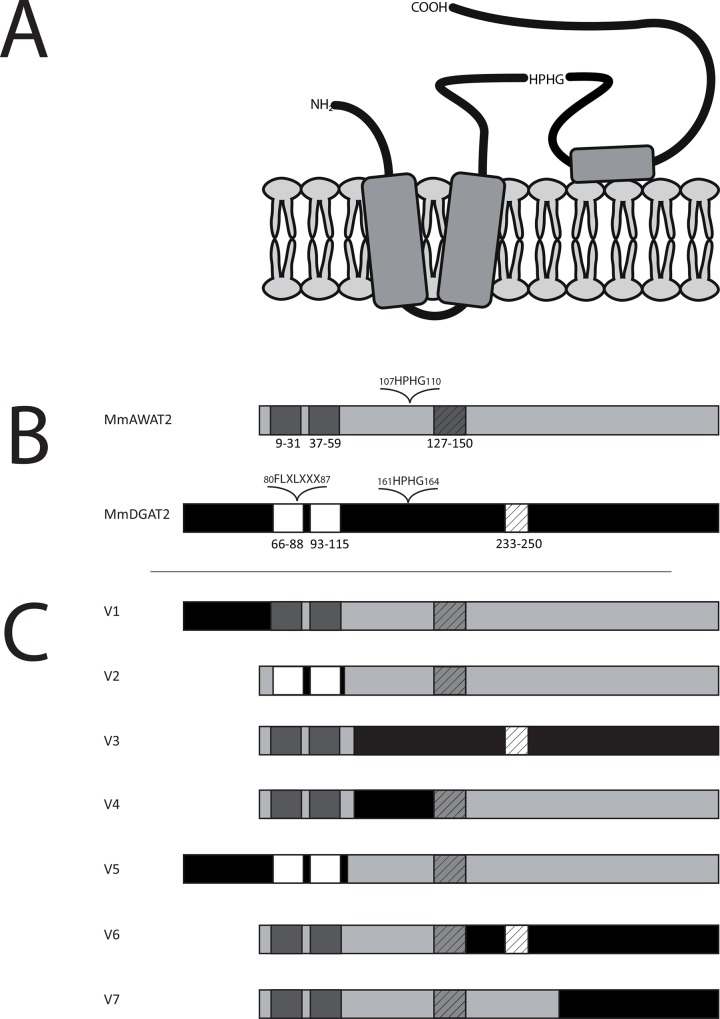
Fig 2. A. Topological model of AWAT2 in accordance to data generated by the services of Phobius [18], TMHMM [16] and SOSUI [17]. According to the model, AWAT2 is predicted to contain an N-terminal cytoplasmic tail that is linked to two TM domains, which are connected by a short linker. The remaining C-terminal sequence forms again a cytosolic domain, which contains the catalytic HPHG motif of the enzyme. A hydrophobic patch that may form a membrane contact is located in the middle of this domain. B. Predicted domain structures of mouse AWAT2 and mouse DGAT2. The conserved TM domains (dark grey/white boxes), the hydrophobic patch (hatched boxes), the active site motif HPHG and the putative neutral lipid binding motif “FLXLXXX” of DGAT2 are indicated. C. Domain swap variants of mouse AWAT2 and mouse DGAT2.
Again, the conserved TM domains (dark grey/white boxes) and the hydrophobic patch (hatched boxes) are indicated. The sequences of mouse AWAT2 and mouse DGAT2 were used to construct seven domain swap variants (V1-V7), in which different parts of mouse AWAT2 were exchanged for the respective parts of mouse DGAT2. Mouse DGAT2 derived parts are shown in black (non-TM domains) and in white (TM-domains), respectively.