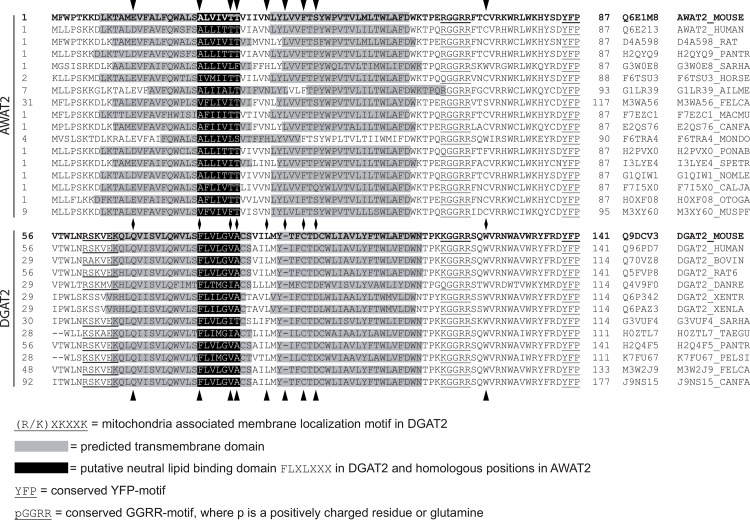
Fig 7. Alignment of the N-terminal part of vertebrate-derived AWAT2 and DGAT2 sequences.
Vertebrate-derived sequences were obtained from the UniProt database [37] and aligned using the Clustal Omega tool [38]. The membrane topology was analyzed by using the SOSUI tool [17]. Predicted TM domains are highlighted in gray, whereas parts of the sequence corresponding to the putative neutral lipid binding domain “FLXLXXX” in mouse DGAT2 are highlighted in black. The conserved motifs pGGRR and YFP are underlined. Mouse DGAT2 and AWAT2, which were used in this study, are printed in bold. In case of mouse DGAT2, the indicated TM structure represents the actual topology determined by Stone et al. 2006 [19]. Besides an abbreviation for each enzyme, also the respective UniProt-identifier is listed. A set of 10 conserved amino acid positions were identified, that were different between DGAT2 and AWAT2 sequences. 9 of these positions are in the shown region and marked by arrow heads.