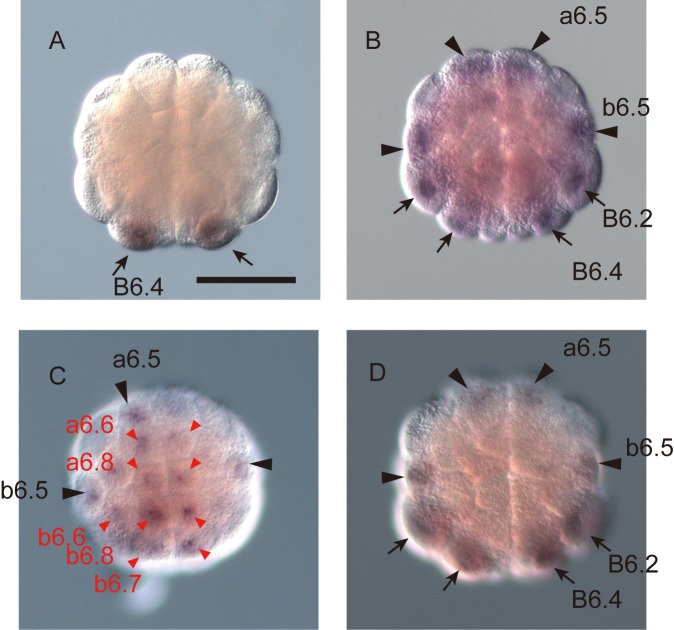
Fig 4. Efna.d signaling plays the key role in patterning of the ectoderm.
(A) Otx is not expressed in a morphant for Fgf9/16/20, Admp, and Gdf1/3-r, as previously reported [4]. (B) Otx is specifically expressed in the neural lineage of morphants for Fgf9/16/20, Admp, and Gdf1/3-r incubated with 1 ng/mL human bFGF and 100 ng/mL human BMP4, although no differential inputs of Fgf9/16/20, Admp and Gdf1/3-r are expected. (C) Otx expression is observed not only in the neural lineage but also in the epidermal lineage of morphants for Fgf9/16/20, Admp, Gdf1/3-r, and Efna.d incubated with bFGF and BMP4. (D) Otx is expressed specifically in the neural lineage of embryos injected with a control morpholino oligonucleotide, which does not have any target mRNAs encoded in the Ciona genome. We injected 15 fmole of each of morpholino oligonucleotides against Fgf9/16/20, Admp, Gdf1/3-r, and Efna.d in (A-C), and 60 fmole of the control morpholino oligonucleotide in (D). Black and red arrowheads indicate the expression of Otx in the neural and epidermal lineages, respectively. Arrows indicate the expression in the vegetal cells.