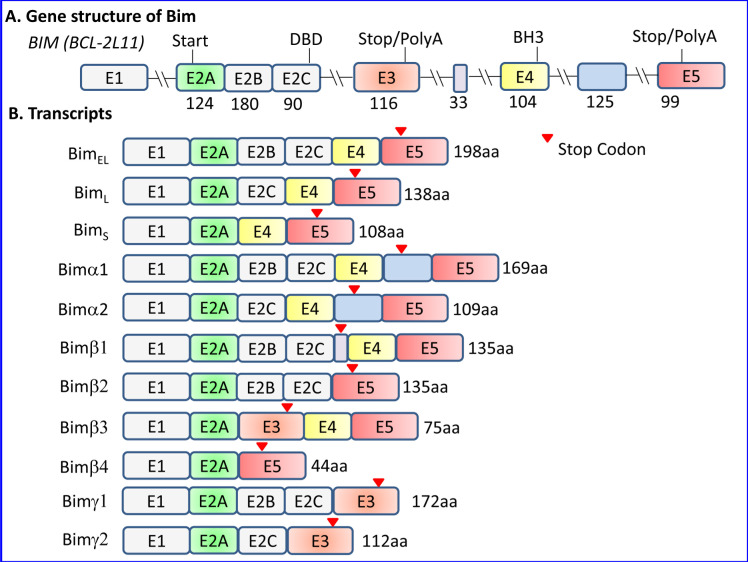
Figure 1. The gene structure of Bim and its major isoform transcripts.
A. Presentation of the Bim (Bcl-2L11) gene structure according to the nomenclature of U et al. [28]. There has been much confusion in the literature concerning the nomenclature of the exon numbers where some research groups have denoted exons E2A, E2B and E2C as exons 2, 3 and 4 respectively, and exons E3, E4 and E5 as exons 5, 6 and 7, respectively. As there is no intron between E2A and E2B, and E2B and E2C, these regions are part of one exon, where intraexonal alternative splicing gives raise to the inclusion or exclusion of the E2B and/or E2C region. DBD - Dynein-binding domain. The BH3 domain is located in exon E4. The numbers beneath the exons refer to the amount of coding nucleotides in each exon. B. Presentation of various Bim isoform transcripts formed by alternative splicing. BimEL, BimL and BimS are the major classical isoforms, but also other isoforms have been identified as described in Section 1.2. Bimα1-2 and Bimβ1-4 were described by U et al. [28], while Bimγ by Ng et al. [31] that was coined Bimγ2 by Anczukow et al. [229]. The latter research group characterized an additional Bimγ isoform (Bimγ1) that also retained the E2B exon [229]. Although Ng et al. [31] claim for a mutual exclusion of exon E3 and E4, the Bimβ3 isoform described by U et al. [28] does contain both exons. As the E3 exon contains a stop codon, its inclusion leads to a truncated protein lacking the pro-apoptotic BH3 domain. The Bim-ABCD, Bim-ACD and Bim-AD described by Marani et al. [9] corresponds to Bimα1, Bimα2 and Bimα3. Bimα3 resembles Bimα2, but lacks E2C.