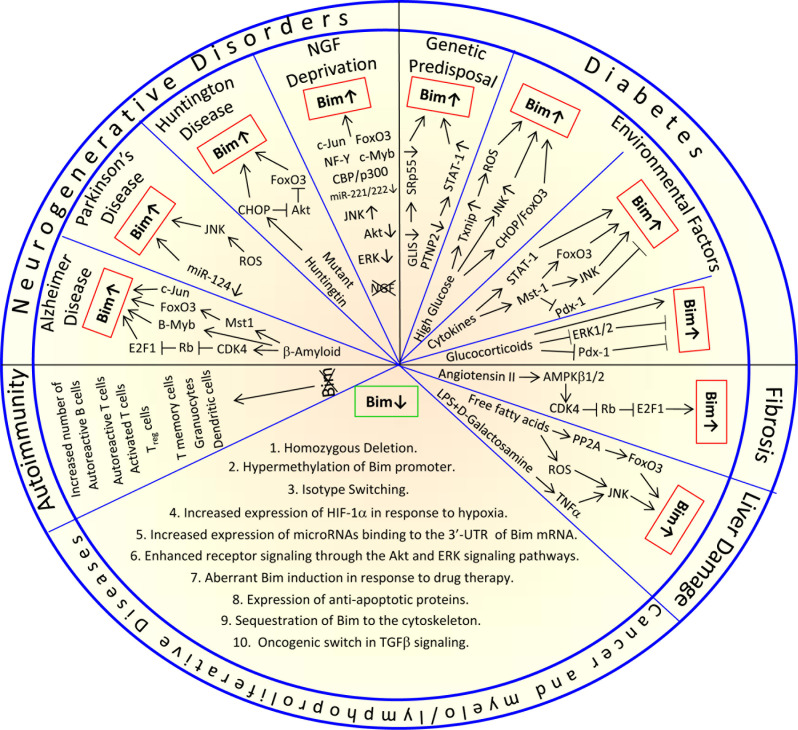
Figure 8. Abberant Bim expression in diseases.
Elevated Bim expression is associated with neuronal degenerative diseases, diabetes, fibrosis and liver damage, while too low or absent Bim expression is associated with cancer (Section 4). Absent Bim expression in the immune system may lead to autoimmune diseases due to lack of elimination of autoreactive immune cells, but is, in part, compensated by an increase in regulatory T cells. Treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and diabetes should aim in preventing Bim expression, while treatment of cancer should aim in increasing Bim expression. Too dramatic increase in Bim during cancer treatment might thus have adverse effects on the nerve system, liver and endocrine system, that needs to be taken into account. Targeting cancer-specific pro-survival pathways would reduce the adverse effects.