Figure 9. Growth factor-mediated cell survival versus apoptosis induction by growth factor deprivation.
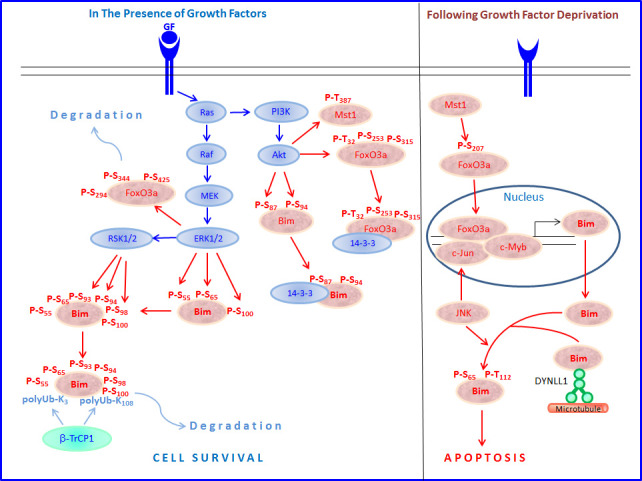
Growth factor receptor activation leads to activation of the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK1/2 and PI3K-Akt pathways that co-operate in inhibiting Bim activity. ERK1/2-mediated phosphorylation of BimEL leads to its subsequent phosphorylation by RSK1/2 and ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation. Akt-mediated phosphorylation of Bim leads to its sequestration to 14-3-3 proteins. Akt also inactivates Mst1 and FoxO3a. Following growth factor withdrawal, the lack of activation of the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK1/2 and PI3K-Akt pathways leads to Mst1 and FoxO3a activation, resulting in the transcriptional upregulation of Bim. In addition, JNK phosphorylates Bim resulting in its activation and apoptosis induction. Inhibition of growth factor receptor signaling (e.g., by EGFR, ALK, c-Met and B-RafV600E inhibitors) is a major cancer-specific targeting strategy that aims to promote Bim-dependent apoptosis.
