Figure 1. Proposed mechanism of action and characterization of fusion proteins.
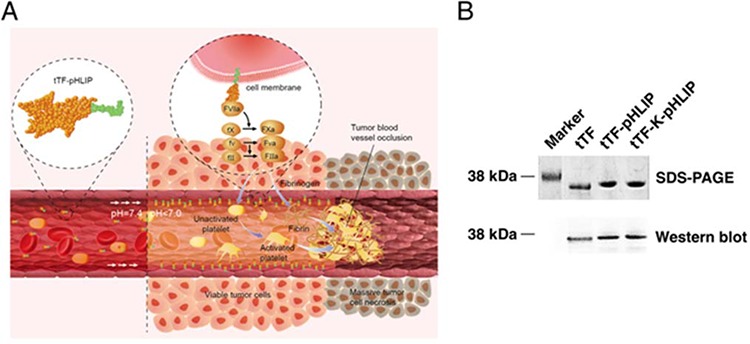
A. Schematic showing the proposed mechanism of action of tTF-pHLIP within tumor blood vessels. tTF-pHLIP freely circulates in the blood at physiological pH, but inserts across the plasma membrane of tumor endothelial cells by virtue of an α-helix (green) which forms at reduced pH in tumor blood vessels. Membrane-bound tTF then triggers the blood coagulation cascade, resulting in thrombosis and consequently tumor vessel infarction and tumor cell necrosis. B. SDS-PAGE and western blot analysis of recombinant purified tTF-pHLIP and control proteins tTF and tTF-K-pHLIP.
