Figure 2. Functional characterization of expressed tTF-pHLIP proteins in vitro.
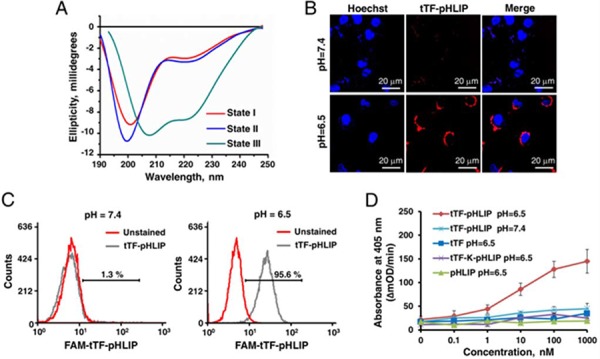
A. Circular dichroism (CD) spectral signals of tTF-pHLIP. The CD spectra of tTF-pHLIP at pH7.4 in the absence (State I) or presence of liposomes (state II) indicated an unstructured configuration of pHLIP peptide. Decreasing the pH to 6.5 (State III) induced the membrane insertion of pHLIP via α-helix formation. B. Confocal images of HUVECs incubated with Alexa 594-labeled tTF-pHLIP (1.24 μM, red) at pH 7.4 (top) or 6.5 (bottom) for 30 min. Cell nuclei were labeled with Hoechst 33342 (blue). C. HUVECs were incubated in PBS at pH 7.4 or 6.5 in the presence (gray) or absence (red) of Alexa 594-labeled tTF-pHLIP (40 μg) at 37°C for 1 hour. Cell surface binding of Alexa 594-labeled tTF-pHLIP was assessed by flow cytometry. D. The ability of tTF-pHLIP and control proteins to facilitate the specific proteolytic activation of factor X by factor VIIa in the presence of HUVECs at pH 7.4 or 6.5 was assessed using a Spectozyme FXa assay. pHLIP was used as negative control. Data represent the mean ± SD of five independent experiments.
