Figure 6. Synergistic inhibitory effects of VTD and etoposide or 5-FU chemotherapeutic drugs on the growth of human colon cancer cells.
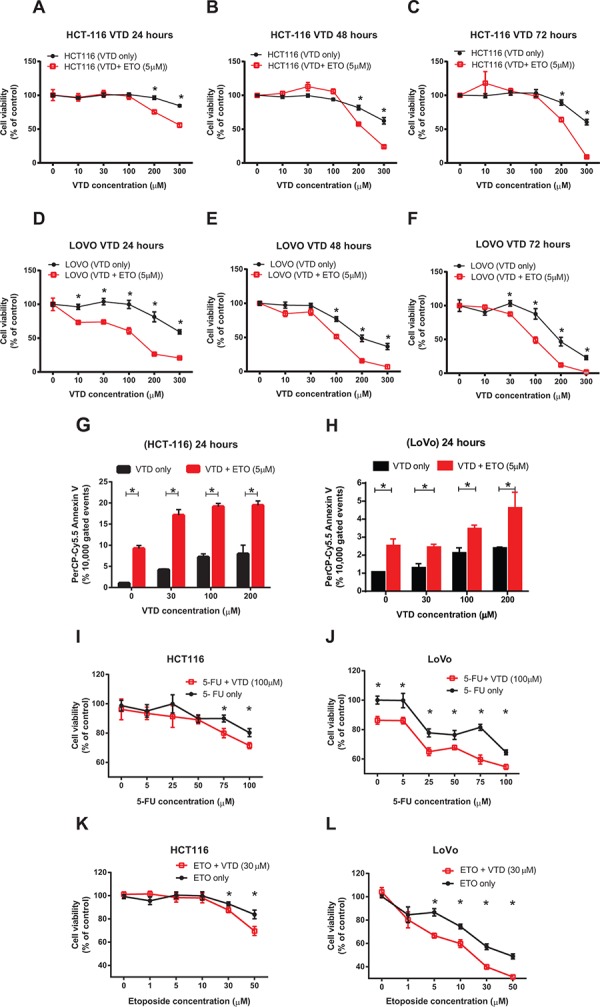
A–C. HCT-116 and D–F. LoVo cells were treated with VTD (10- 300 μM) for 24, 48, and 72 hours. A suboptimal dose of Etoposide (ETO) (5 μM) was added to cells for the last 24 hours only. The viability of cells was determined as % of control (untreated cells) using an MTT assay. The chemotherapeutic drug ETO significantly enhanced the VTD-induced decrease in cell viability of both poorly differentiated (HCT-116) and well-differentiated (LoVo) colon cancer cell lines in a time-dependent manner. G–H. HCT-116 (G) and LoVo (H) cells were treated with VTD (10–200 μM) and a suboptimal dose of ETO (5 μM) for 24 hours. Cells were then stained with Annexin V apoptotic marker. ETO significantly sensitizes both poorly and well-differentiated colon cancer cells to VTD even at 30 μM. I–L. HCT-116 and LoVo cells were treated with different doses of 5-FU (5–100 μM, I-J) and ETO (1–50 μM, K-L) along with VTD (30 μM and 100 μM respectively) for 24 hours. MTT assays showed the treatment with 5-FU and ETO with VTD decreased cell viability at much lower drug doses particularly in LoVo cells. Results were analyzed using CalcuSyn software to calculate the combination index (CI) to confirm and quantify the synergism observed with combination therapies (S6 and S7 and Supplementary Tables 4 and 5). The data is shown as mean ± SEM of three different experiments (n = 3) where *p < 0.001 using Bonferroni's modified student's t-test.
