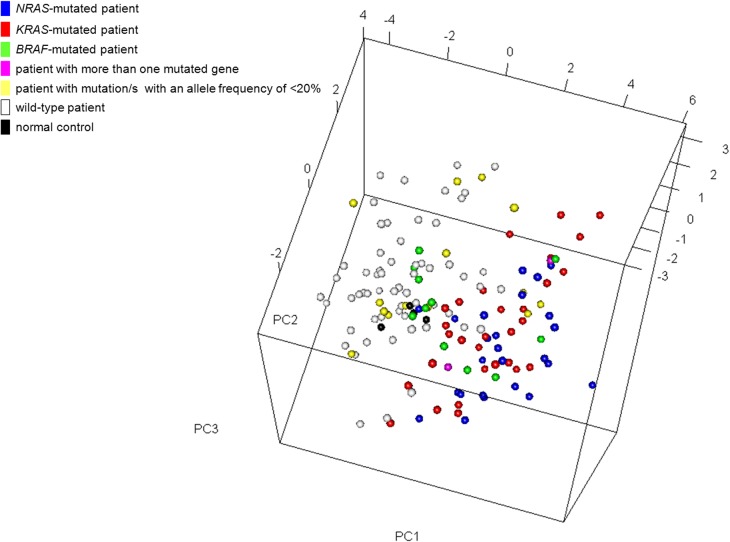
Figure 5. Multidimensional scaling plot using the most significant genes (n = 18) differentially expressed between BRAF/NRAS/KRAS-mutated and wild-type patients.
Each point represents a single sample and is coloured on its type (patient/normal control) and mutation status as measured by sequence analysis. In the case of co-existing mutations of which only one had an allele frequency of >20%, the color corresponds to the gene with the highest mutational load.