Figure 3. EBERs-LMP1 interactive positive feedforward loop amplifies the inflammatory response in NPC cell lines.
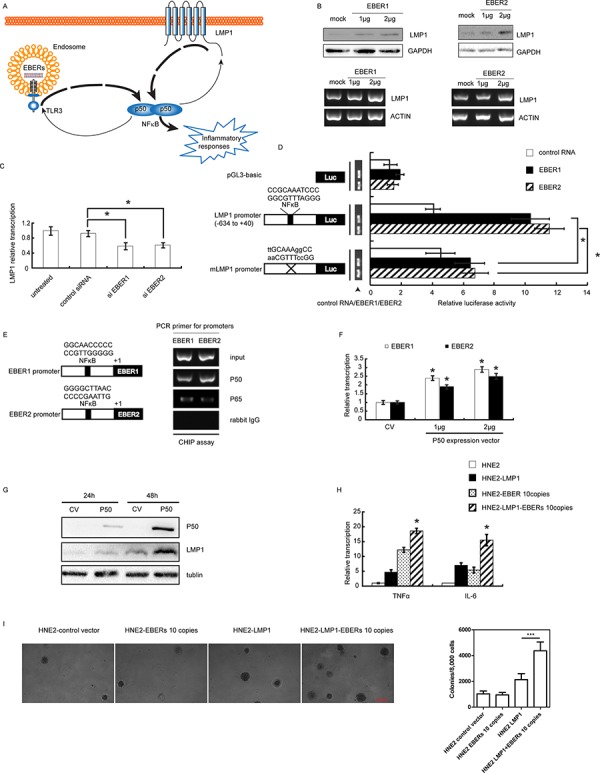
A. Schematic description of a proposed model for EBERs-LMP1 interactive feedfroward loop in promoting cancer-related inflammation. EBERs and LMP1 can both trigger moderate inflammatory response through NFκB as a key node. In addition to the role as an inflammation mediator, NFκB can transcriptionally up-regulate EBERs and LMP1. As a result, EBERs promote LMP1 transcription via NFκB which in turn transcriptionally induce more EBERs expression via NFκB likewise. Consequently, EBERs and LMP1 synergistically generate overwhelming signals to promote NFκB mediated cancer-related inflammation. B. C666–1 cells were challenged with in vitro transcribed EBER1 or EBER2 for 24 h and LMP1 expression was determined by western blotting and RT-PCR. C. LMP1 transcription level was assayed by qPCR in C666–1 cells treated with EBER1 [14]or EBER2 siRNAs for 48 h [14]. D. In vitro transcribed EBER1 or EBER2 was co-transfected with Renilla reniformis expression plasmids driven by LMP1 promoter with or without mutation in NFκB binding site and pGL3-basic was used as a control. 24 h later, luciferase activity was measured. Wild-type or mutated sequences of NFκB binding site in LMP1 promoter are indicated and the mutated bases are in lowercase. E. ChIP assay was performed to measure occupancy of EBER promoter by NFκB using antibodies against p50 and p65 in C666–1 cells. Putative NFκB binding sites of EBER1 and EBER2 are shown in the left panel. F. C666–1 cells were transiently transfected with p50 expression plasmid for 48 h, and EBER1 or EBER2 transcripts was determined by qPCR. G. LMP1 expression was analyzed by western blotting in C666–1 at 24 and 48 h post transfection with p50 expression plasmid. H. mRNA levels of TNFα and IL-6 were determined in HNE2 and HNE2 cells stably expressing EBERs or/and LMP1. I. Soft agar assay was conducted to demonstrate the anchor-independent growth ability conferred by LMP1 or/and EBERs. Experiments were conducted three times and the data were expressed as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 versus mock treated group in (F) or between assigned groups as indicated in (C), (D) and (I) In (H) *P < 0.05 between HNE2-LMP1-EBERs cells and any other groups for TNFα and IL-6. CV, control vector.
