Figure 7. Re-expression of wild-type and mutant forms of eIF3b and eIF3c restores knockdown-induced cell size defects, independently of S6K1-activity.
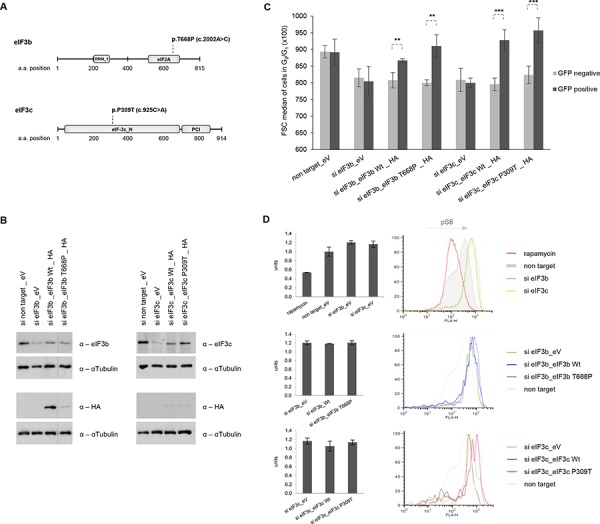
A. Schematic representation of eIF3b and eIF3c protein secondary structure including annotated Pfam-A protein domains. The substitution missense mutation of eIF3b (p.T668P) is located in the eIF2A region and of eIF3c (p.P309T) in the N terminal region. RRM_1, RNA recognition motif; eIF2A, eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF2A; eIF-3c_N, eukaryotic initiation factor 3 subunit 8 N terminus; PCI, PCI domain (Cosmic database). B. IMR-90 cells depleted for eIF3b and eIF3c were transfected with empty vector (eV), wild-type (Wt) eIF3b, Wt eIF3c or the corresponding mutants. To avoid interference in detection of eIF3b, eIF3c and HA-tagged proteins due to similar protein size, the same lysates were detected on separate membranes. C. A control vector carrying GFP-spectrin was co-transfected in all settings used. Cell size was measured in GFP-negative (untransfected fraction) and GFP-positive cells (transfected fraction). Representative bar diagrams out of two independent experiments are shown. Error bars correspond to means ± SD. D. Phosphorylation levels of S6 (S240/244) protein were determined by phospho-specific flow cytometry in GFP-positive cells using the same co-transfection setting as in (C) Representative bar diagrams and histogram overlays out of two independent experiments are shown.
