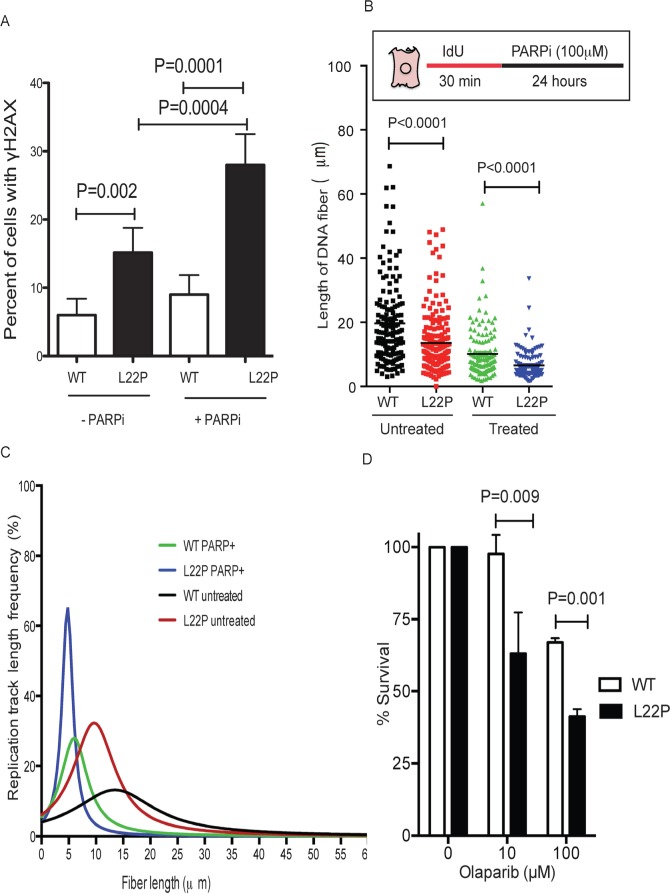
Figure 6. L22P variant of DNA polymerase beta confers sensitivity to PARP1 inhibitors compared to WT cells.
A. Estimated percentages of γH2AX in L22P and WT of cells treated with or without PARP1 inhibitor. B. The distribution of NDS in untreated WT (n = 110) and L22P-expressing cells (n = 120) and PARP1 inhibitor treated wild type (n = 123) and L22P-expressing cells (n = 122). Note that the schematic representation of replication tracts in WT and L22P-expressing GES cells were first labeled with Idu (25m) for 30 minutes (red line), then treated with 100mM PARP1 inhibitor ((PARPi) olaparib) for 24 hour (black line) then processed for DNA fiber spread as described in Materials and Methods. DNA fiber lengths were measured using NIH imageJ and data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism. C. The replication fork track length frequency in WT and L22P-expressing cells treated with PARP1 inhibitor. D. Clonogenic survival assays were conducted with GES-1 cells expressing WT or L22P Pol β in two different concentration of PARP1 inhibitor (10μM and 100μM). Data were analyzed two ways of ANOVA using GraphPad Prism.