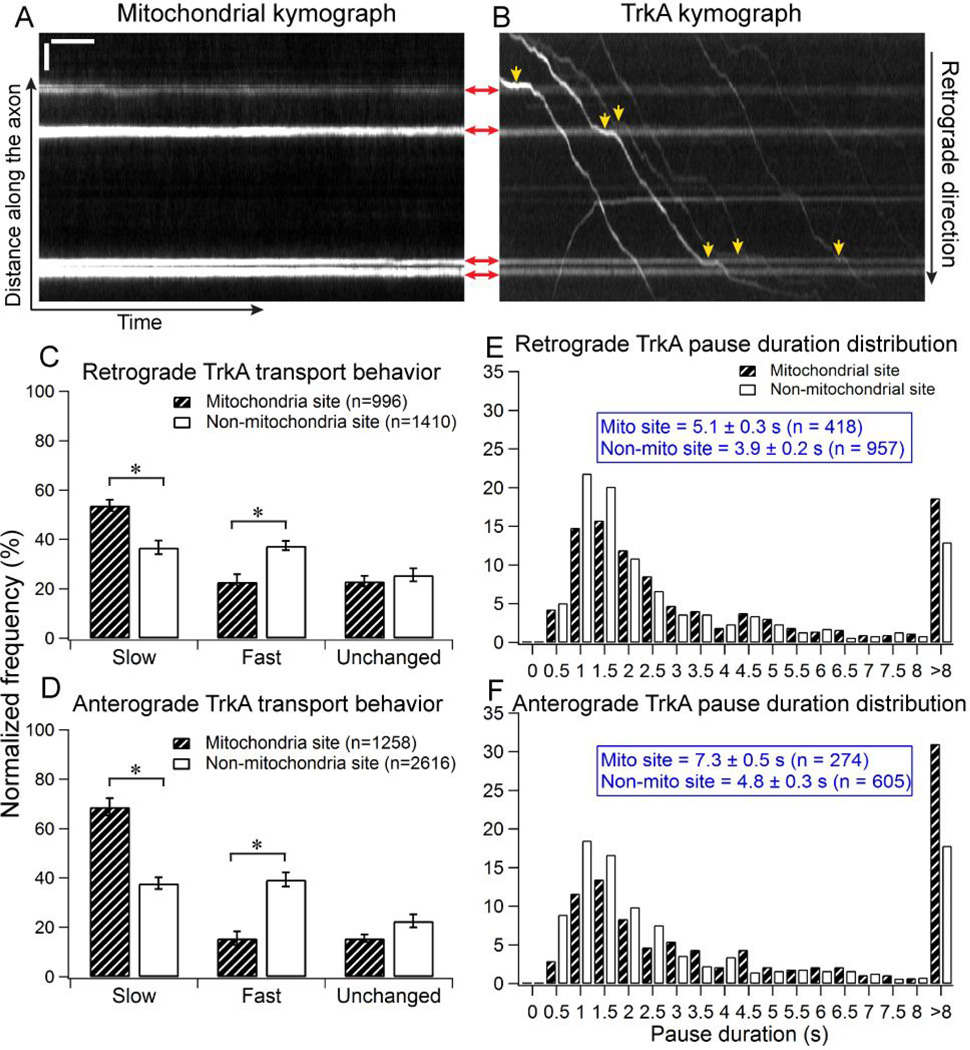
Figure 2.
Moving TrkA cargos slow down when crossing stationary mitochondria in DRG axons. DRG neurons are co-transfected with TrkA-mCherry and Mito-YFP. (A) A representative mitochondrial kymograph. Horizontal lines indicate the stationary mitochondria in the axon. (B) The kymograph of TrkA cargos in the same axon. Shadows of the four mitochondria in the axon can also be seen on TrkA kymograph. Red arrows show the positions of mitochondriain both the mitochondrial and TrkA kymographs. Yellow arrowheads indicate the regions where TrkA cargos clearly slow down when crossing the stationary mitochondria in the axon. Horizontal bar, 5s.Vertical bar, 5µm. (C–D) Quantification of TrkA transport behavior in the retrograde direction (C) and the anterograde direction (D). Data were cumulated from 7 independent experiments. Bootstrapping (10 sets of 300 randomly selected events) was performed to calculate the standard deviation. Error bars represents standard deviation. Statistical significance was assessed using Student’s t-test, p<0.001. (E–F) The distribution of pause duration for TrkA cargos at mitochondrial sites compared to control sites that are not associated with mitochondria. Data were cumulated from 7 independent experiments.