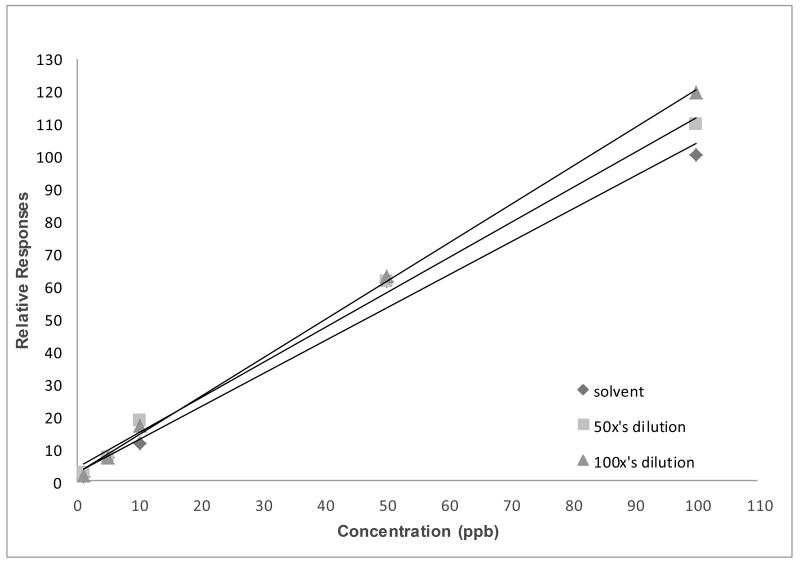
Figure 6. Varying slope values of PBDE-47 in different matrix dilutions.
Note: Extraction of PBDE-47 from brain tissue was done while homogenizing the tissue sample with a mixture of hexane and acetone (1:1 ratio). The extractant was later purified using Florisil cartridges (6 cc, 500 mg) (Restek Corp, Bellefonte, CA). Target analytes were eluted from the cartridge using hexane. Chromatographic separation and analysis was performed by an Agilent 7000 GC-MS/MS with electron impact ionization interface (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany). The system was fitted with a deactivated silica guard column (0.250 mm internal diameter (ID)) (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA USA) connected to a HP-5MS analytical column (15 m × 0.250 ID × 0.25 μm film thickness, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA USA). One milliliter of extractant was injected into the system under pulsed splitless mode and with an injector temperature of 250°C. The helium carrier gas flow rate was 1.8 mL/min. Gradient temperature program (from 70 °C to 315°C) was used during chromatographic separation. The interface, source, and quadrupole temperatures were set to 315°C, 315°C, and 150°C, respectively. The total run time was 16 minutes. Quantitative MS/MS transition for PBDE-47 was m/z485.6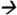 326.0@25V CE while the MS/MS transition for isotopic PBDE-47 analouge was m/z497.5
326.0@25V CE while the MS/MS transition for isotopic PBDE-47 analouge was m/z497.5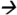 338.0@25V CE.
338.0@25V CE.