Figure 1.
Chronic Replication Stress Induces Epigenetic Instability of BU-1
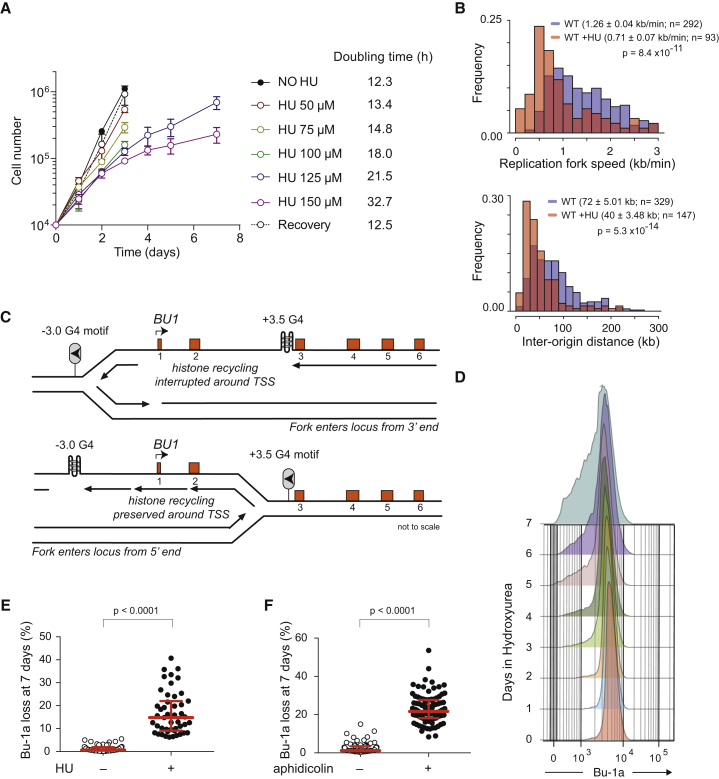
(A) Doubling time of wild-type DT40 cells in different concentrations of HU. Recovery indicates the growth rate of cells that had been cultured for 1 week in 150 μM HU and then transferred to drug-free medium. Error bars indicate SD of three experiments.
(B) Replication dynamics of DT40 cells after 3 days of growth in 150 μM HU determined by DNA molecular combing. See also Figure S1A. For fork speed, the bin size is 0.2 kb/min with untreated wild-type cells in blue overlaid in red with results from HU-treated cells. For the inter-origin distance, the bin size is 15 kb. The median fork rate and interorigin distance are given ± SEM. The probability that the HU-treated distribution is different from untreated was calculated with the Mann-Whitney test.
(C) Schematic of the model for G4-induced, replication-dependent epigenetic instability of the Bu-1 locus (adapted from Schiavone et al., 2014). The BU-1 locus is bidirectionally replicated (Schiavone et al., 2014).
(D) Bu-1alow cells appear stochastically as a function of time as cells divide in HU. Flow cytometry for Bu-1a was performed daily on a population of wild-type DT40 cells growing in 150 μM HU.
(E) Fluctuation analysis for Bu-1a loss in multiple parallel cultures grown in 150 μM HU. Each symbol represents the percentage of Bu-1alow cells in an individual culture after 7-day growth with or without HU (150 μM).
(F) Fluctuation analysis for Bu-1a loss following 7-day growth in low-dose (150 μM) aphidicolin.