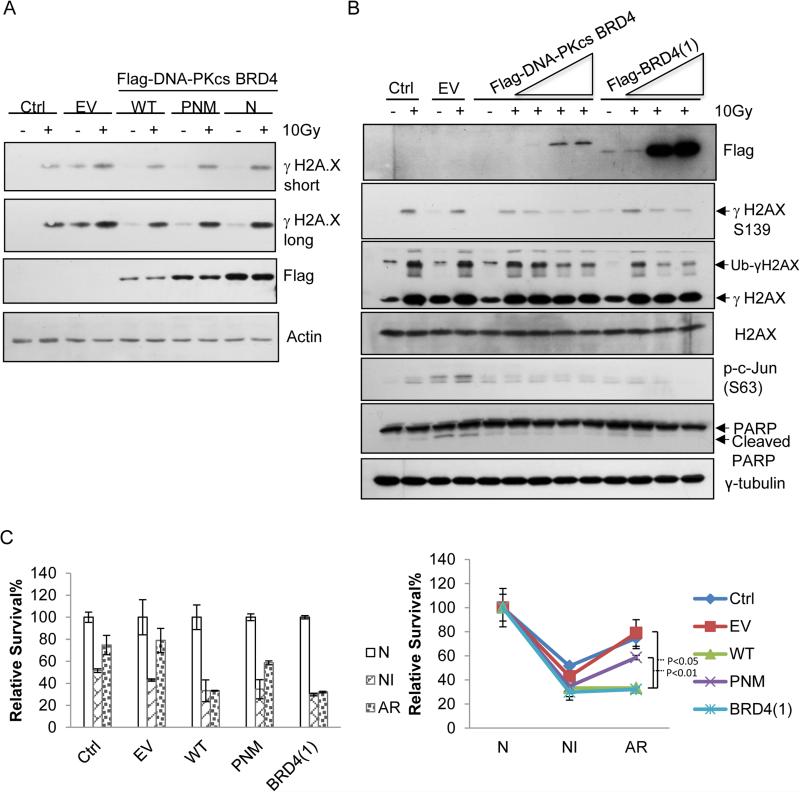
Figure 5. The non-canonical DNA-PKcs-BRD defines its kinase activity specifically for phosphorylating Ser139 and the associated cell fate decision.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of the effects of the exogenously expressed, empty vector (EV), wild-type DNA-PKcs-BRD (WT, aa2070-2200) or the mutants of single (N2174A or ‘N’) or triple (P2110A/N2174A/M2185A or ‘PNM’) site-substitution(s) within the BRD of DNA-PKcs on the 10Gy-induced level of γSer139 on H2AX. (B) Immunoblot analysis of the effects of the exogenously expressed, empty vector (EV), or wild-type DNA-PKcs-BRD (WT) or BRD4 on the propensity of the acute-IR-irradiated U2OS cells. Multiple apoptotic markers including phosphor-ser63 of c-Jun, cleaved PARP were assayed by the indicated antibodies. (C) Clonogenic survival analysis of the effects of the exogenously expressed, empty vector (EV), wild-type DNA-PKcs-BRD (WT) or the mutants of single (N) or triple (PNM) site-substitution(s) within the BRD of DNA-PKcs or BRD4 on the survival of differently irradiated cells. Following the transfection of each given vector the U2OS cells were treated respectively with either ‘non-irradiation (N), or 2 Gy acute-irradiation (NI), or 0.1Gy-priming for 24 hours then 2Gy-irradiation (AR).