Figure 1.
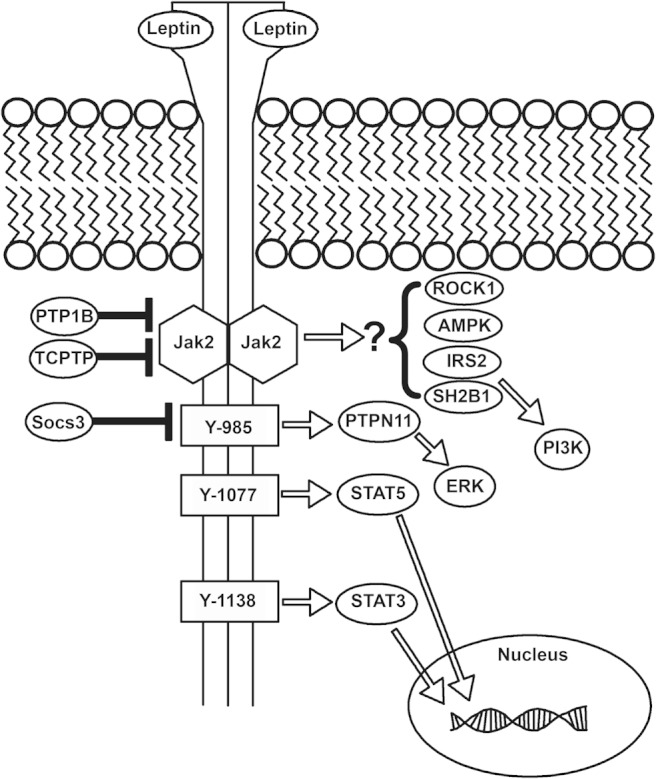
LepRb signaling. Leptin binds to the extracellular domain of LepRb, activating the associated Jak2 tyrosine kinase and promoting the Jak2-mediated phosphorylation of tyrosine residues 985, 1077, and 1138 of LepRb (note, numbering is that of the murine receptor). Phosphorylated Tyr985 recruits PTPN11, which initiates the ERK signaling cascade. Phosphorylated Tyr1077 and Tyr1138 recruit STAT5 and STAT3, respectively, permitting their trafficking to the nucleus to mediate the control of cognate gene expression. In addition, mechanisms that limit LepRb signaling have been defined: Socs3, whose expression is increased by leptin, binds to phosphorylated Tyr985 to blunt LepRb signaling. Also, the tyrosine phosphatases, PTP1B and TCPTP, dephosphorylate Jak2 and/or LepRb to terminate LepRb signaling. In addition, Rho kinase 1, adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase, insulin receptor substrate (IRS)2, and SH2B1 have been shown to act downstream of LepRb, although the mechanisms by which LepRb controls these pathways have yet to be defined.
