Abstract
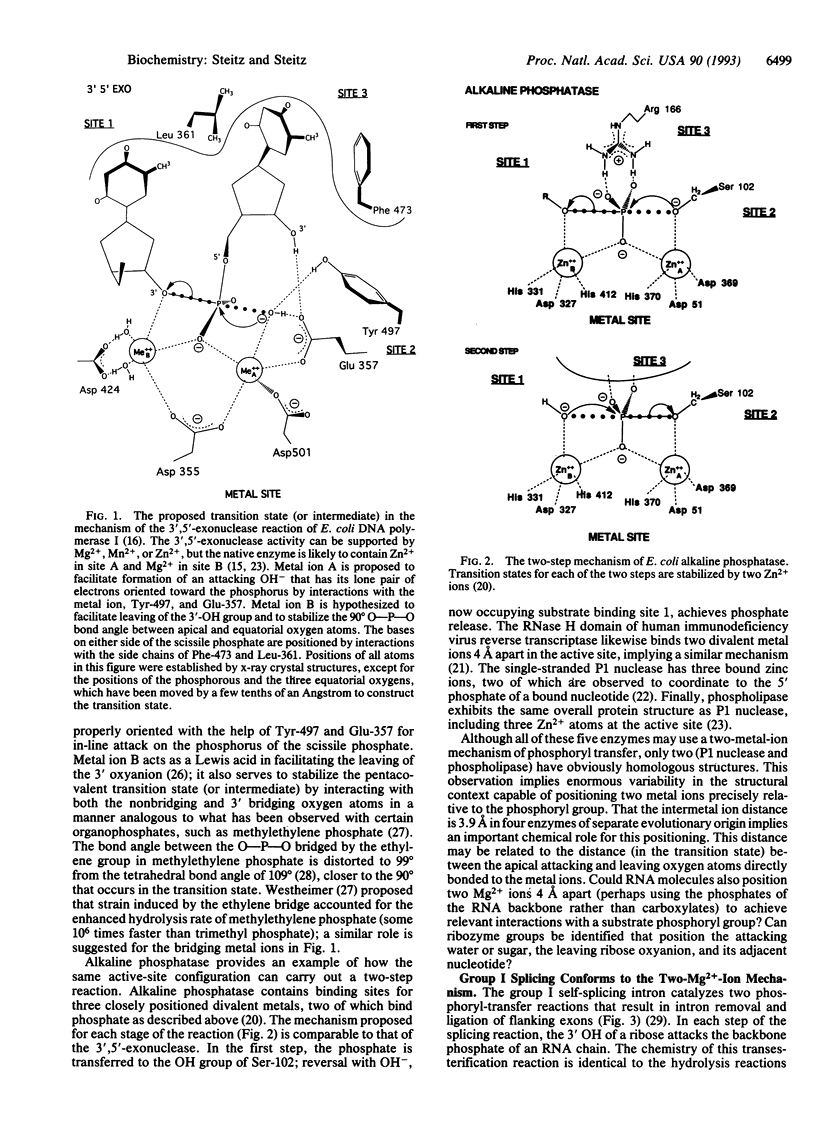
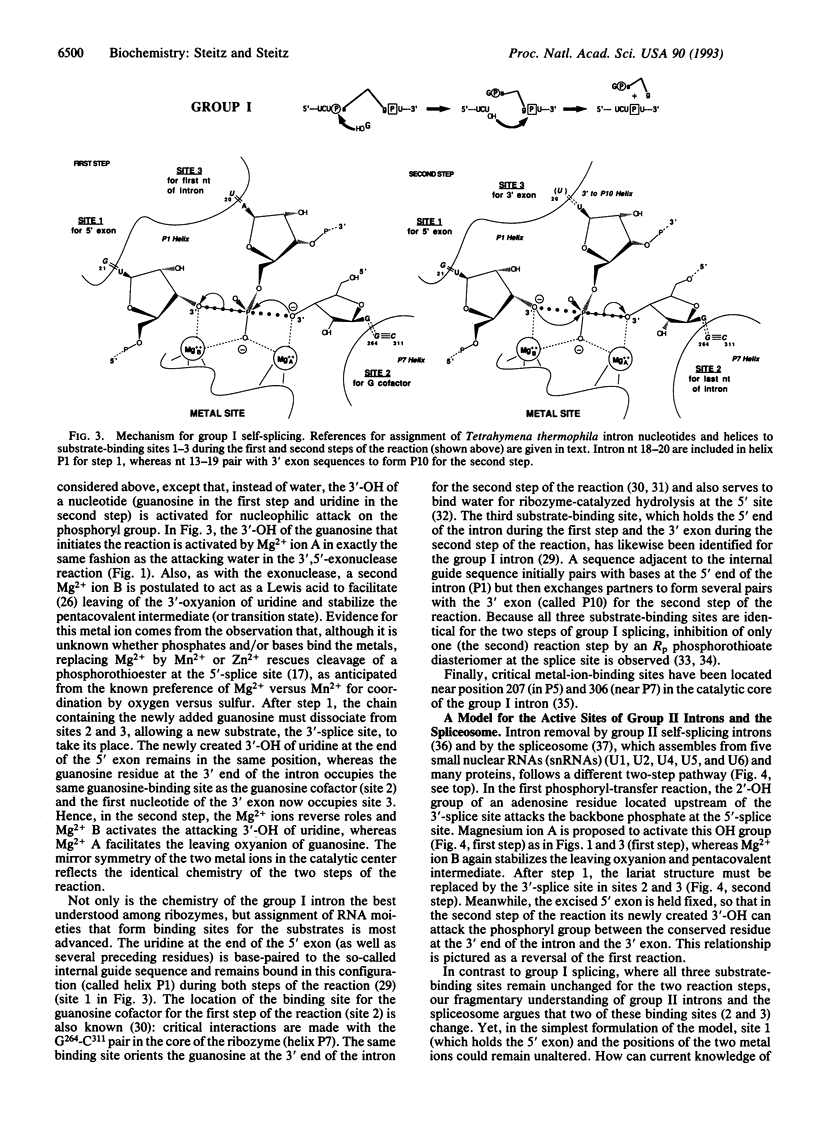
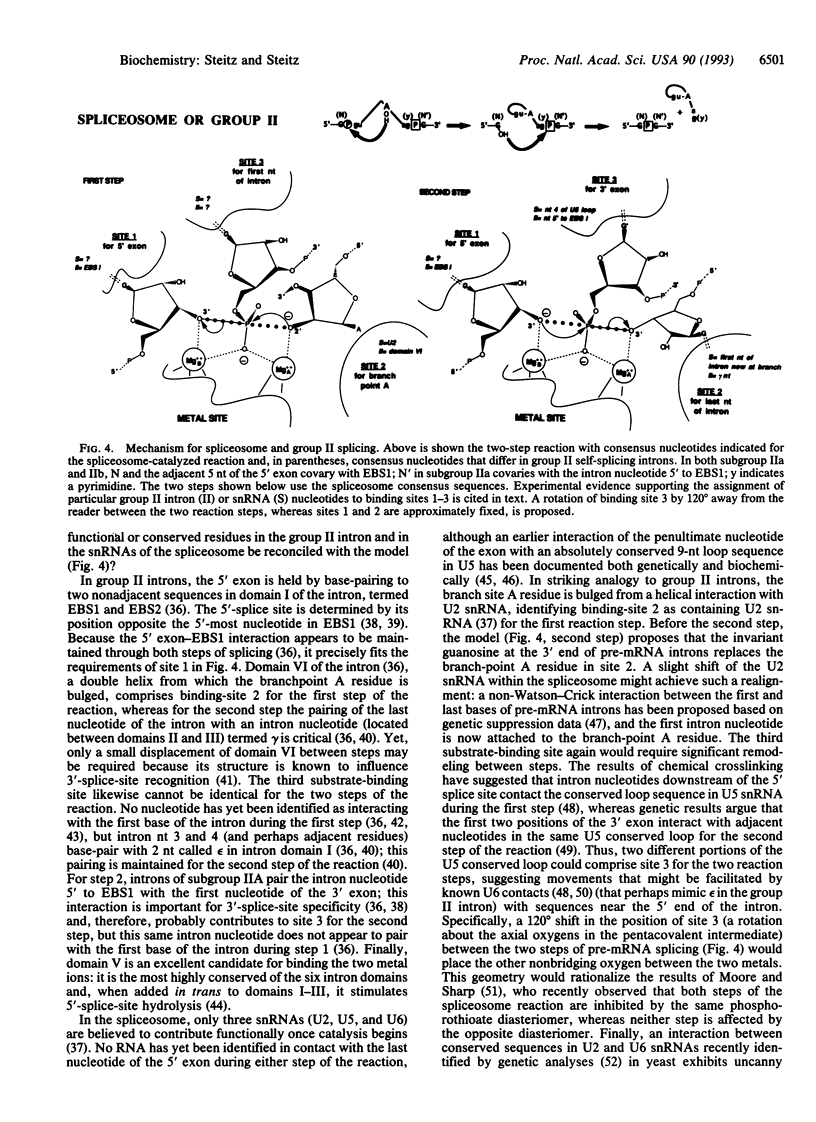
A mechanism is proposed for the RNA-catalyzed reactions involved in RNA splicing and RNase P hydrolysis of precursor tRNA. The mechanism postulates that chemical catalysis is facilitated by two divalent metal ions 3.9 A apart, as in phosphoryl transfer reactions catalyzed by protein enzymes, such as the 3',5'-exonuclease of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. One metal ion activates the attacking water or sugar hydroxyl, while the other coordinates and stabilizes the oxyanion leaving group. Both ions act as Lewis acids and stabilize the expected pentacovalent transition state. The symmetry of a two-metal-ion catalytic site fits well with the known reaction pathway of group I self-splicing introns and can also be reconciled with emerging data on group II self-splicing introns, the spliceosome, and RNase P. The role of the RNA is to position the two catalytic metal ions and properly orient the substrates via three specific binding sites.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman S., Kirsebom L., Talbot S. Recent studies of ribonuclease P. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):7–14. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.7916700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Perrotta A. T. Group I intron self-splicing with adenosine: evidence for a single nucleoside-binding site. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):434–437. doi: 10.1126/science.2017681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beese L. S., Steitz T. A. Structural basis for the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I: a two metal ion mechanism. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):25–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow D. M., Steitz T. A. X-ray diffraction studies of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:63–100. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.000431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgin A. B., Pace N. R. Mapping the active site of ribonuclease P RNA using a substrate containing a photoaffinity agent. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4111–4118. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07633.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. Self-splicing of group I introns. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:543–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. The chemistry of self-splicing RNA and RNA enzymes. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1532–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.2438771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Zaug A. J., Grabowski P. J. In vitro splicing of the ribosomal RNA precursor of Tetrahymena: involvement of a guanosine nucleotide in the excision of the intervening sequence. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):487–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian E. L., Yarus M. Metal coordination sites that contribute to structure and catalysis in the group I intron from Tetrahymena. Biochemistry. 1993 May 4;32(17):4475–4480. doi: 10.1021/bi00068a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. F., 2nd, Hostomska Z., Hostomsky Z., Jordan S. R., Matthews D. A. Crystal structure of the ribonuclease H domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1991 Apr 5;252(5002):88–95. doi: 10.1126/science.1707186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire V., Freemont P. S., Sanderson M. R., Beese L., Friedman J. M., Joyce C. M., Steitz T. A. Genetic and crystallographic studies of the 3',5'-exonucleolytic site of DNA polymerase I. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):199–201. doi: 10.1126/science.2832946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire V., Grindley N. D., Joyce C. M. The 3'-5' exonuclease of DNA polymerase I of Escherichia coli: contribution of each amino acid at the active site to the reaction. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):17–24. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07916.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P. S., Friedman J. M., Beese L. S., Sanderson M. R., Steitz T. A. Cocrystal structure of an editing complex of Klenow fragment with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8924–8928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Gardiner K., Marsh T., Pace N., Altman S. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Haydock K., Allen L., Altman S. Metal ion requirements and other aspects of the reaction catalyzed by M1 RNA, the RNA subunit of ribonuclease P from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 8;25(7):1509–1515. doi: 10.1021/bi00355a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Lumelsky N., Altman S. Specific interactions in RNA enzyme-substrate complexes. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1578–1584. doi: 10.1126/science.2480641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C. Messenger RNA splicing in yeast: clues to why the spliceosome is a ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):157–163. doi: 10.1126/science.1853200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough E., Hansen L. K., Birknes B., Jynge K., Hansen S., Hordvik A., Little C., Dodson E., Derewenda Z. High-resolution (1.5 A) crystal structure of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):357–360. doi: 10.1038/338357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Jacquesson-Breuleux N. Splice site selection and role of the lariat in a group II intron. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jun 5;219(3):415–428. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Michel F. Base-pairing interactions involving the 5' and 3'-terminal nucleotides of group II self-splicing introns. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 5;213(3):437–447. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80206-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K. A., Dietrich R. C., Perlman P. S. Group II intron domain 5 facilitates a trans-splicing reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2361–2366. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazakov S., Altman S. Site-specific cleavage by metal ion cofactors and inhibitors of M1 RNA, the catalytic subunit of RNase P from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9193–9197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim E. E., Wyckoff H. W. Reaction mechanism of alkaline phosphatase based on crystal structures. Two-metal ion catalysis. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 20;218(2):449–464. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90724-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. H., Cech T. R. Three-dimensional model of the active site of the self-splicing rRNA precursor of Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8788–8792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. H., Suddath F. L., Quigley G. J., McPherson A., Sussman J. L., Wang A. H., Seeman N. C., Rich A. Three-dimensional tertiary structure of yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA. Science. 1974 Aug 2;185(4149):435–440. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4149.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles J. R. Enzyme-catalyzed phosphoryl transfer reactions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:877–919. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legault P., Herschlag D., Celander D. W., Cech T. R. Mutations at the guanosine-binding site of the Tetrahymena ribozyme also affect site-specific hydrolysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6613–6619. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhani H. D., Guthrie C. A novel base-pairing interaction between U2 and U6 snRNAs suggests a mechanism for the catalytic activation of the spliceosome. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):803–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90556-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSwiggen J. A., Cech T. R. Stereochemistry of RNA cleavage by the Tetrahymena ribozyme and evidence that the chemical step is not rate-limiting. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):679–683. doi: 10.1126/science.2470150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Hanna M., Green R., Bartel D. P., Szostak J. W. The guanosine binding site of the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):391–395. doi: 10.1038/342391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Umesono K., Ozeki H. Comparative and functional anatomy of group II catalytic introns--a review. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):5–30. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Westhof E. Modelling of the three-dimensional architecture of group I catalytic introns based on comparative sequence analysis. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 5;216(3):585–610. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90386-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. W., Schweyen R. J., Schmelzer C. Selection of cryptic 5' splice sites by group II intron RNAs in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7383–7395. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Norman C. U5 snRNA interacts with exon sequences at 5' and 3' splice sites. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):743–754. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A., Norman C. Mutations in yeast U5 snRNA alter the specificity of 5' splice-site cleavage. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90413-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace N. R., Smith D. Ribonuclease P: function and variation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3587–3590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Siliciano P. G. Evidence for an essential non-Watson-Crick interaction between the first and last nucleotides of a nuclear pre-mRNA intron. Nature. 1993 Feb 18;361(6413):660–662. doi: 10.1038/361660a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccirilli J. A., Vyle J. S., Caruthers M. H., Cech T. R. Metal ion catalysis in the Tetrahymena ribozyme reaction. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):85–88. doi: 10.1038/361085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertus J. D., Ladner J. E., Finch J. T., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Clark B. F., Klug A. Structure of yeast phenylalanine tRNA at 3 A resolution. Nature. 1974 Aug 16;250(467):546–551. doi: 10.1038/250546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawa H., Abelson J. Evidence for a base-pairing interaction between U6 small nuclear RNA and 5' splice site during the splicing reaction in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11269–11273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzer C., Müller M. W. Self-splicing of group II introns in vitro: lariat formation and 3' splice site selection in mutant RNAs. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):753–762. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D., Pace N. R. Multiple magnesium ions in the ribonuclease P reaction mechanism. Biochemistry. 1993 May 25;32(20):5273–5281. doi: 10.1021/bi00071a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Oefner C. Structure of DNase I at 2.0 A resolution suggests a mechanism for binding to and cutting DNA. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):620–625. doi: 10.1038/321620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh E., Waring R. B. A phosphorothioate at the 3' splice-site inhibits the second splicing step in a group I intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6303–6309. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchimaru T., Uebayasi M., Tanabe K., Taira K. Theoretical analyses on the role of Mg2+ ions in ribozyme reactions. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):137–142. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volbeda A., Lahm A., Sakiyama F., Suck D. Crystal structure of Penicillium citrinum P1 nuclease at 2.8 A resolution. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1607–1618. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07683.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallasch C., Mörl M., Niemer I., Schmelzer C. Structural requirements for selection of 5'- and 3' splice sites of group II introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3307–3314. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassarman D. A., Steitz J. A. Interactions of small nuclear RNA's with precursor messenger RNA during in vitro splicing. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1918–1925. doi: 10.1126/science.1411506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. R., Sontheimer E. J., Steitz J. A. Site-specific cross-linking of mammalian U5 snRNP to the 5' splice site before the first step of pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2542–2553. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M. How many catalytic RNAs? Ions and the Cheshire cat conjecture. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):31–39. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


