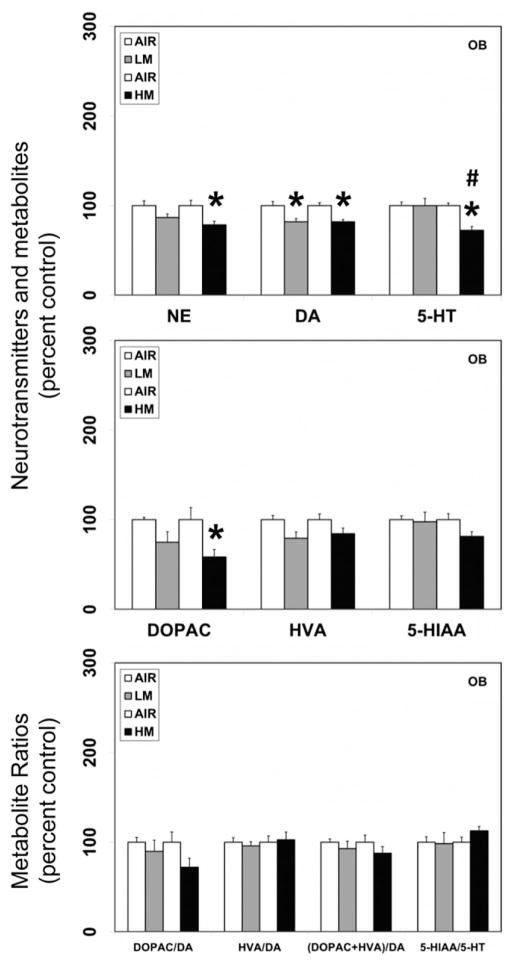
Figure 1.
Resistance spot welding aerosols alter the levels of neurotransmitters and their metabolites in the olfactory bulb (OB). Rats were exposed to LM or HM aerosols (25 mg/m3 × 4 h/day) by whole-body inhalation for 13 days. At 1 day post-exposure, the levels of norepinephrine (NE), dopamine (DA), serotonin (5-HT), 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC), homovanillic acid (HVA) and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) were measured by HPLC-EC. Following normalization to an internal standard (isoproterenol), the concentration of each compound was calculated as ng/mg total protein. The metabolite ratios, DOPAC/DA, HVA/DA (DOPAC+HVA/DA) and 5-HIAA/DA were then calculated from the individual measures. The values are expressed as percent of air-exposed controls and graphical representations are mean±SE (n=4/group) for the low metal exposure experiments and (n=6/group) for the high metal exposure experiments. *Indicates significant change from corresponding air-exposed control (p<0.05). #Indicates significantly different from LM-exposed group.