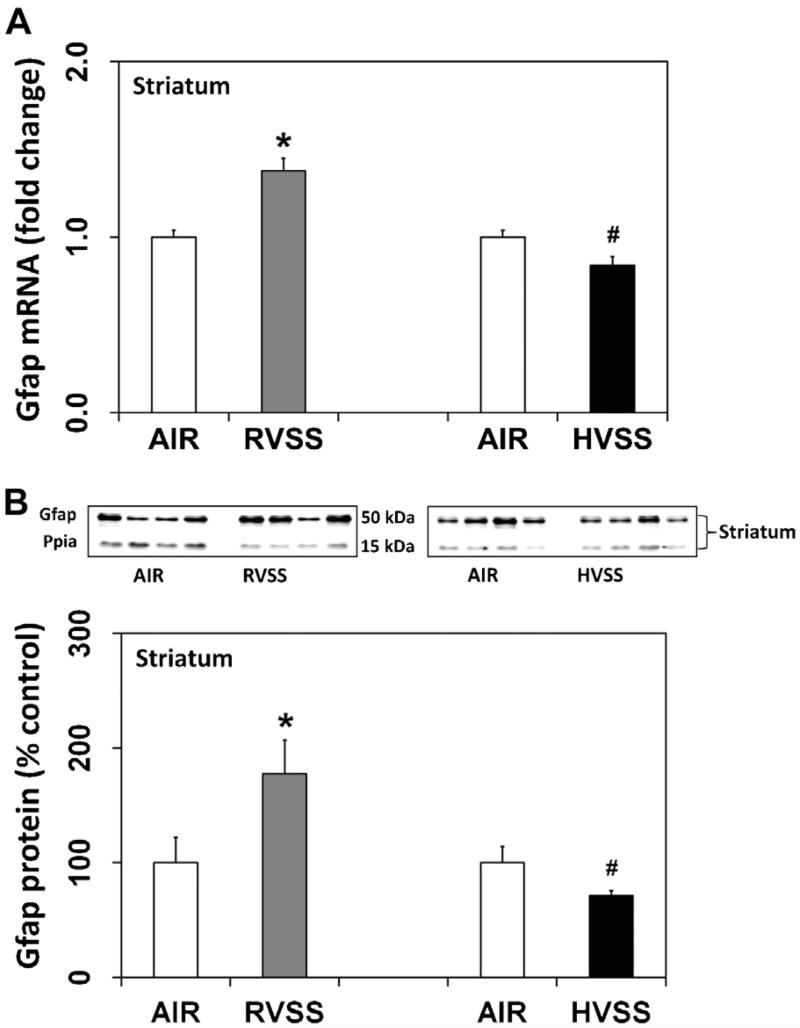
Fig. 8.
Effect of RVSS and HVSS fume particulates on Gfap gene expression in the striatum. Rats were exposed by whole-body inhalation (40 mg/m3; 3 h/day × 5 d/week × 2 weeks; for a total of 10 days) to fume particulates generated by gas–metal arc-stainless steel (GMA-SS) welding at standard/regular voltage (25 V; RVSS) or at high voltage (30 V; HVSS). (A) At 1 day post-exposure, the expression of Gfap mRNA in the STR was assayed TaqMan® real-time PCR. Following normalization to the endogenous control beta actin (Actb), the values are expressed as fold change from air-exposed controls. Graphical representations are Mean ± SE (n = 6/group). (B) At 1 day post-exposure, the expression of Gfap protein in the STR was determined by immunoblot analysis. Following normalization to the endogenous control cyclophilin A (Ppia), the values are expressed as percent of air-exposed controls. Graphical representations are Mean ± SE (n = 4/group). * indicates significant change from corresponding air-exposed control (P < 0.05). # indicates significantly different from RVSS group.