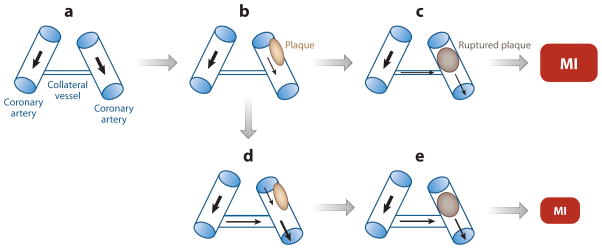
Figure 3.
Remodeling of a collateral blood vessel in response to coronary artery stenosis. (a) Two major coronary arteries, which are connected by an undeveloped collateral vessel, are shown. (b) Atherosclerotic plaque formation (tan oval ) results in stenosis of one artery. (c) Plaque rupture results in complete arterial obstruction (brown oval ), leading to a large myocardial infarction (MI). (d ) Remodeling of the collateral vessel to increase luminal diameter results in increased blood flow. (e) When plaque rupture occurs, the reduction in blood flow is mitigated, resulting in a smaller area of infarction. Black arrows denote the direction and relative magnitude of blood flow.