Fig. 4.
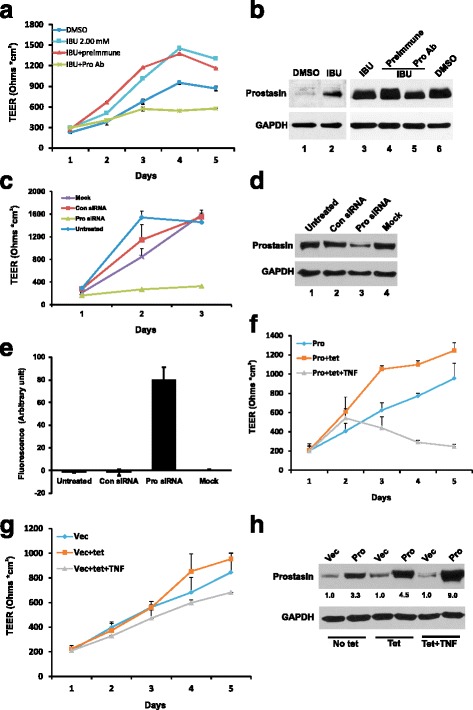
Transepithelial electric resistant (TEER) measurement and permeability assay. The B6Tert-1 cells were first treated with 2 mM ibuprofen for 24 h and seeded in Transwells to develop cell-cell contact and tight junctions. The TEER was measured using an EVOM device as described in the Methods. a TEER of B6Tert-1 cells treated with DMSO (used as a solvent control), or ibuprofen, or a prostasin antibody (Pro Ab), or a pre-immune rabbit serum (used as a control). ANOVA: p < 0.05. b Western blot analysis of prostasin expression in B6Tert-1 cells treated with 2 mM ibuprofen for 24 h (Lanes 1–2); or grown in Transwells for 5 days (Lanes 3–6). c TEER of B6Tert-1 cells treated with a prostasin-specific siRNA. Untreated: cells were not treated with any reagent; Con siRNA: a random siRNA used as a control; Pro siRNA: the prostasin-specific siRNA; Mock: cells were treated with the transfection reagent Lipofectamine 2000 only. ANOVA: p < 0.05. d Western blot analysis of prostasin expression in B6Tert-1 cells after silencing prostasin expression. e Permeability of B6Tert-1 cells to FITC-dextran (n = 3). The prostasin siRNA-treated cells had the most FITC-dextran in the basal medium of the cells. ANOVA: p < 0.05. f TEER of B6Tert-1 cells expressing different amounts of prostasin. Pro: prostasin; tet: tetracycline; TNF: tumor necrosis factor (alpha). ANOVA: p < 0.05. g TEER of B6Tert-1 cells harboring the vector alone (Vec). ANOVA: p > 0.05. h Western blot analysis of prostasin expression in B6Tert-1 under tet or tet + TNF-α treatment. The numbers under each lane indicate the fold change of the expression as compared to the vector control (Vec)
