Fig. 1.
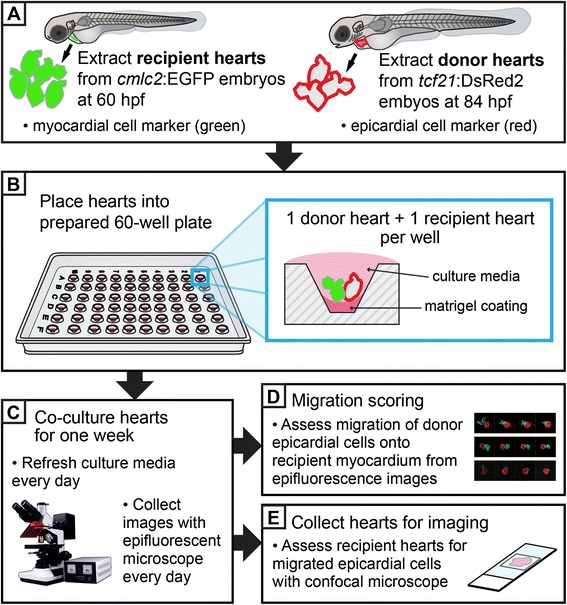
Overview schematic of the in vitro co-culture assay for assessing migration of epicardial cells. (a) Hearts are extracted from embryonic zebrafish. Recipient hearts are collected from cmlc2:EGFP embryos, which have a green myocardial cell marker. These hearts are extracted at 60 hpf, prior to the migration of epicardial progenitor cells (EPCs), such that extracted hearts have bare myocardia. Donor hearts are collected from tcf21:DsRed2 embryos, which have a red epicardial cell marker. These hearts are extracted at 84 hpf, after migration of EPCs has begun, such that extracted hearts carry some epicardial cells that are actively spreading. Recipient and/or donor embryos may be pre-treated before isolation of hearts according to experimental design. For example, in this report the recipient hearts came from embryos that were injected with MOs affecting expression of specific genes. (b) Collected hearts are placed in a prepared 60-well cell culture dish. Each well has been pre-coated with a thin layer of matrigel basement membrane mix, and contains one donor and one recipient heart, submerged in culture medium. The donor and recipient hearts are arranged such that the ventricles are in contact. (c) Donor and recipient hearts are co-cultured for one week. Each day the culture media is refreshed and each culture well is imaged with an epifluorescence microscope. (d) Epifluorescence images are scored in a blinded fashion for the migration of donor epicardial cells onto recipient myocardial cells. (e) After 7 days in culture, heart samples are fixed and stained for immunohistochemistry. Each sample is analyzed with confocal microscopy for presence of donor epicardial cells that have migrated onto recipient myocardia to verify positive migration
