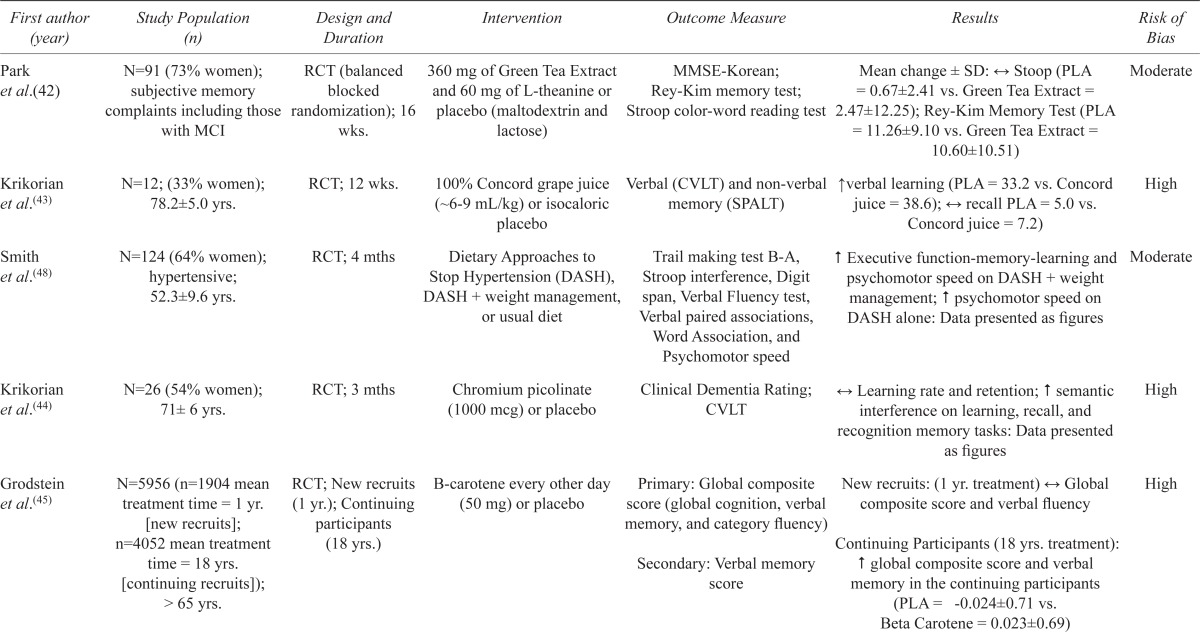
TABLE 4.
Studies of other nutritional or dietary supplements on cognitive function
| First author (year) | Study Population (n) | Design and Duration | Intervention | Outcome Measure | Results | Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Park et al.(42) | N=91 (73% women); subjective memory complaints including those with MCI | RCT (balanced blocked randomization); 16 wks. | 360 mg of Green Tea Extract and 60 mg of L-theanine or placebo (maltodextrin and lactose) | MMSE-Korean; Rey-Kim memory test; Stroop color-word reading test | Mean change ± SD: ↔ Stoop (PLA = 0.67±2.41 vs. Green Tea Extract = 2.47±12.25); Rey-Kim Memory Test (PLA = 11.26±9.10 vs. Green Tea Extract = 10.60±10.51) | Moderate |
| Krikorian et al.(43) | N=12; (33% women); 78.2±5.0 yrs. | RCT; 12 wks. | 100% Concord grape juice (∼6–9 mL/kg) or isocaloric placebo | Verbal (CVLT) and non-verbal memory (SPALT) | ↑ verbal learning (PLA = 33.2 vs. Concord juice = 38.6); ↔ recall PLA = 5.0 vs. Concord juice = 7.2) | High |
| Smith et al.(48) | N=124 (64% women); hypertensive; 52.3±9.6 yrs. | RCT; 4 mths | Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH), DASH + weight management, or usual diet | Trail making test B-A, Stroop interference, Digit span, Verbal Fluency test, Verbal paired associations, Word Association, and Psychomotor speed | ↑ Executive function-memory-learning and psychomotor speed on DASH + weight management; ↑ psychomotor speed on DASH alone: Data presented as figures | Moderate |
| Krikorian et al.(44) | N=26 (54% women); 71± 6 yrs. | RCT; 3 mths | Chromium picolinate (1000 mcg) or placebo | Clinical Dementia Rating; CVLT | ↔ Learning rate and retention; #semantic interference on learning, recall, and recognition memory tasks: Data presented as figures | High |
| Grodstein et al.(45) | N=5956 (n=1904 mean treatment time = 1 yr. [new recruits]; n=4052 mean treatment time = 18 yrs. [continuing recruits]); > 65 yrs. | RCT; New recruits (1 yr.); Continuing participants (18 yrs.) | B-carotene every other day (50 mg) or placebo | Primary: Global composite score (global cognition, verbalmemory, and category fluency) Secondary: Verbal memory score |
New recruits: (1 yr. treatment) ↔ Global composite score and verbal fluency Continuing Participants (18 yrs. treatment): ↑ global composite score and verbal memory in the continuing participants (PLA = -0.024±0.71 vs. Beta Carotene = 0.023±0.69) |
High |
| Rossom et al.(49) | N=4143; 71 yrs. (65–80); women | RCT; Mean follow-up of 7.8 yrs. | 2 tablets/d (1,000mg of calcium carbonate and 400 IU of vitamin D3) or placebo | Primary: development of dementia or MCI Secondary: 3MSE, Digit Span Forward and backwards, Primary Mental Abilities Vocabulary Test, Card Rotation Test, Letter and Semantic fluency test, California Verbal Learning Test, the Benton Visual Retention Test, and Finger Tapping Test |
Primary: ↔ Incidence of cognitive impairment (Hazard ratio: 1.11, 95% CI, 0.71 – 1.74 for dementia) Secondary: ↔ 3MSE; ↔ on any domain-specific cognitive scores |
Moderate |
| Wolters et al.(46) | N=220 women; 60–91 yrs. | RCT; 6 mths | Vitamin and mineral capsule (150 mg vitamin C, 50 mg magnesium, 36 mg vitamin E, 34 mg niacin, 16 mg pantothenic acid, 9 mg B-carotene, 3.4 mg pyridoxine, 3.2 mg riboflavin, 2.4 mg thiamine, 400 μg folic acid, 200 μg biotin, 60 µg selenium, and 9 μµg cobalamin) or placebo (soy oil) | Symbol search test, Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, and pattern recognition and intelligence | Mean (5–95th percentiles): ↔ Pattern recognition (PLA = 7.4 (5.0–10.0) vs. multivitamin = 7.6 (5.0–10.0)) and intelligence (PLA = 110 (90.0–129) vs. multi-vitamin = 109 (93.4–131)); ↑ symbol search test (PLA = 33.0 (23–42) vs. multi-vitamin = 35.0 (25–48) | Moderate |
| Macpherson et al.(47) | N=56 women; 64–82 yrs. | RCT; 16 wks. | Multivitamin (contains folic acid, B6, B12), antioxidant and mineral formula with added herbal and antioxidant plant extracts (Swiss Women’s Ultivite 50+) or placebo | Primary: memory and attention composite score Secondary: Simple Reaction Time; Complex Reaction Time; Immediate and Delayed Recognition Memory; Stroop Congruent; Contextual Recognition Memory; CVLT-II |
Primary data is presented as figures. ↑ Spatial working memory; ↔ any other cognitive test | Moderate |
↑ = significantly better (p <.05) in the experimental condition; ↔ = no difference between conditions; RCT = randomized controlled trial; MMSE = Mini-Mental State Examination; IU = international units; MCI = mild cognitive impairment; TICS-M = telephone interview for cognitive status – modified; CVLT = California Verbal Learning Test.