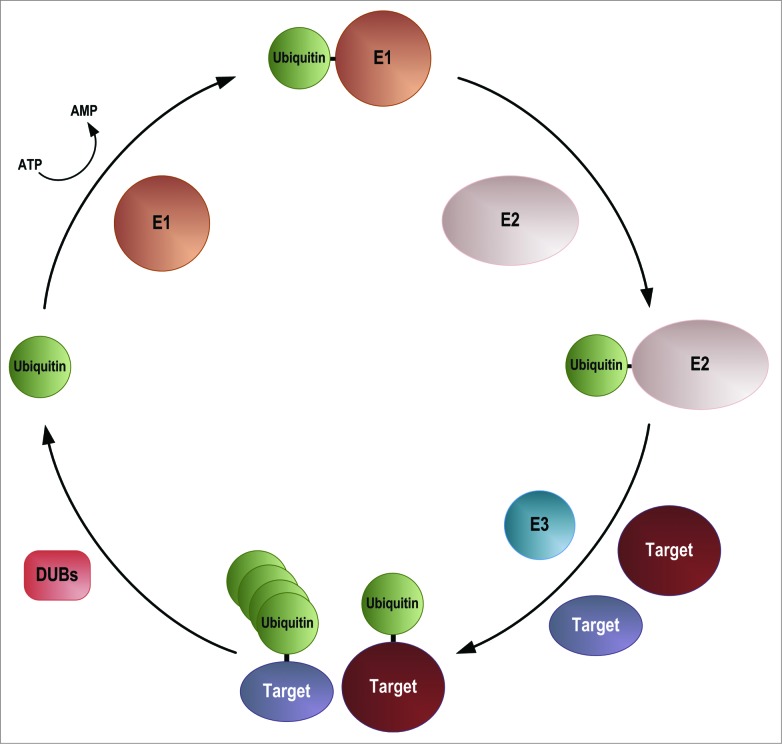
Figure 2.
Ubiquitylation pathway. E1 = Ubiquitin activating enzyme, E2 = ubiquitin conjugating enzyme, E3 = ubiquitin ligase, DUB = deubiquitylating enzyme. Ubiquitin is activated by the formation of a ubiquitin-adenylate before forming a thioester bond with a cysteine residue in the E1 ubiquitin activating enzyme. Ubiquitin is passed to an E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzyme, again forming a thioester bond. Target proteins are recognized by E3 ubiquitin ligases, either directly or via an adaptor, and ubiquitin is attached via the formation of an ε-amino bond. Ubiquitin can be attached to target proteins either as a monomer, or in the form of ubiquitin chains. Ubiquitin can be removed from target proteins by the action of one of a number of DUBs.