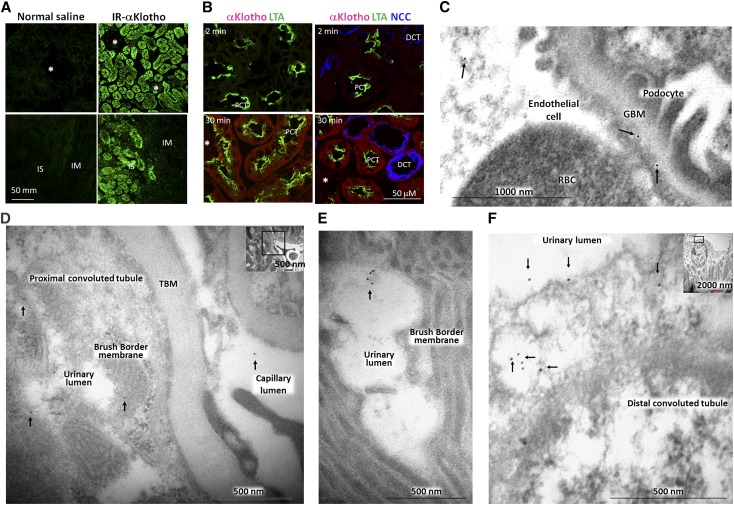
Figure 4.
The distribution of exogenous recombinant mouse αKlotho in the kidney. (A) Infrared dye labeled αKlotho (IR-αKlotho) or normal saline was intraperitoneally injected into normal rats. Two hours later, kidney was harvested, sectioned, and imaged with IR microscope. (B) αKlotho labeled with two types of fluorescent dye: Alexa 555 C2 Maleimide (λex 555 nm, λem 565 nm) and TAMRA-SE (λex 546 nm, λex 579 nm) was intravenously injected into normal rats, and kidneys were collected at specific time points and subjected to immunofluorescent staining for αKlotho, NaCl cotransporter (NCC), and Lotus-Tetragonolobus lectins (LTA). Asterisks depict glomerulus. DCT: distal convoluted tubule; IM: inner medulla; IS: inner strip of outer medulla; PCT: proximal convoluted tubule. (C–F). αKlotho protein was intraperitoneally injected into homozygous αKlotho-deficient mice and the kidneys were harvested for immunogold electron microscopy. Representative electron micrographs of exogenous αKlotho in (C) glomeruli, (D, E) proximal tubules, (F) distal tubules. Arrows indicate gold particle (labeled αKlotho protein).