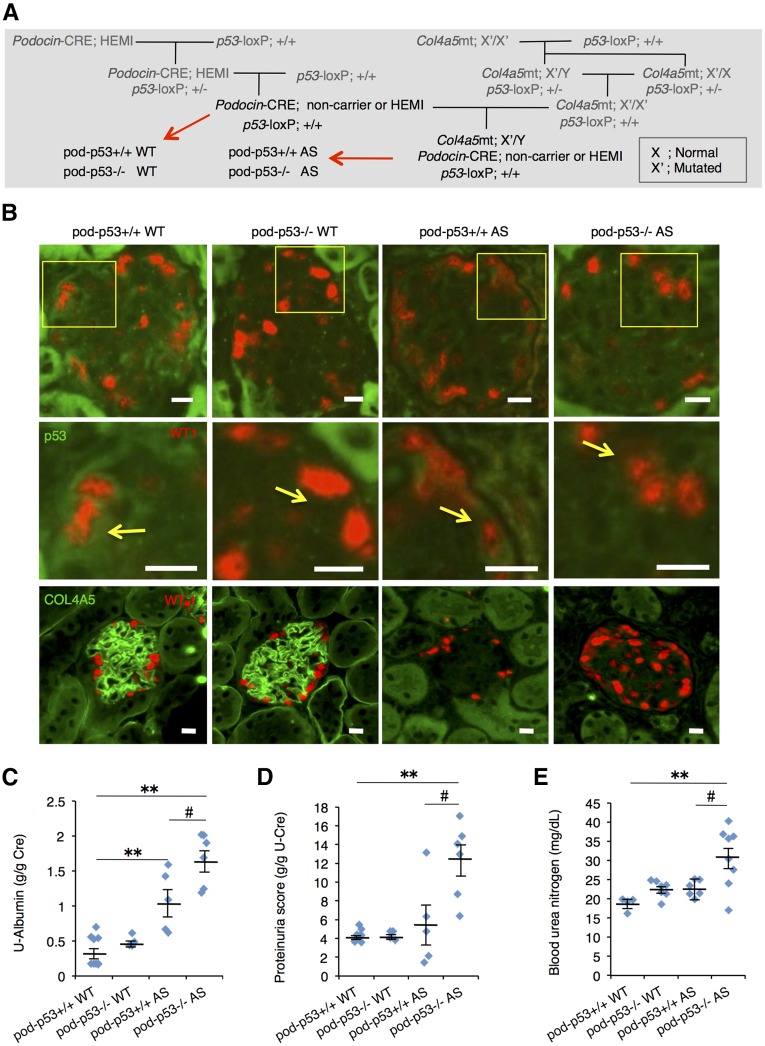
Figure 4.
Podocyte-specific p53 deletion promotes AS-induced renal dysfunction. (A) Mating procedure to generate podocyte-specific p53-deficient WT and AS mice. Each littermate group of pod-p53+/+ or −/− WT and pod-p53+/+ or −/− AS was used for the following experiments. (B) Frozen sections of renal cortex harvested from 15-week-old mice were stained for immunofluorescence with antibodies against p53 (green) and WT-1 (red) or with type IV collagen A5 (green) and WT-1 (red). Fields in yellow box are magnified in the panel below. Yellow arrows indicate p53 expression in WT-1-positive cells. Scale bars, 10 μm. (C, D) Urine samples from 15-week-old mice were assessed for (C) U-Albumin and (D) proteinuria scores. (mean±SEM, n=4–9). (E) BUN score in 15-week-old mice was measured (mean±SEM, n=4–8). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 versus pod-p53+/+ WT; #P<0.05 versus pod-p53+/+ AS.