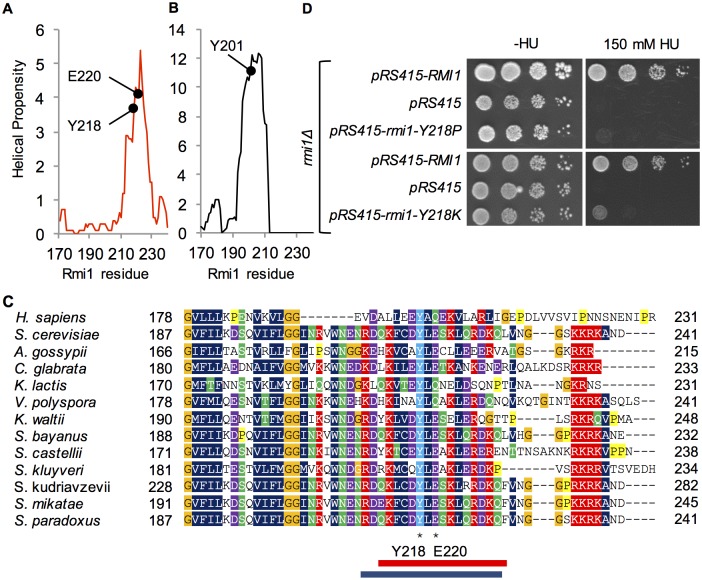
Fig 4. Mutational analysis of the C-terminal region of increased helical propensity.
A and B, Yeast Rmi1 and human Rmi1-N, the N-terminal 240-residue region of human Rmi1 that is most similar to yeast Rmi1, have comparable predicted structure in the far C-terminus. Y218 is in the same predicted helix as E220 and has a potential equivalent in Y201 in human Rmi1. C, PhylomeDB alignment of Rmi1 C-termini from different yeast species reveals a highly conserved tyrosine at position 218. The corresponding region of human Rmi1 (residues 178–231) was manually aligned to the yeast Rmi1 phylome. The position of the predicted α-helix in yeast Rmi1 is indicated by a red rectangle below the alignment. The corresponding α-helix defined by Y201 in the crystal structure of human Rmi1 (PDB: 4CGY) is indicated by a blue rectangle. D, like rmi1-E220P, rmi1-Y218P and rmi1-Y218K mutants fail to complement the hydroxyurea hypersensitivity of an Δrmi1 mutant.