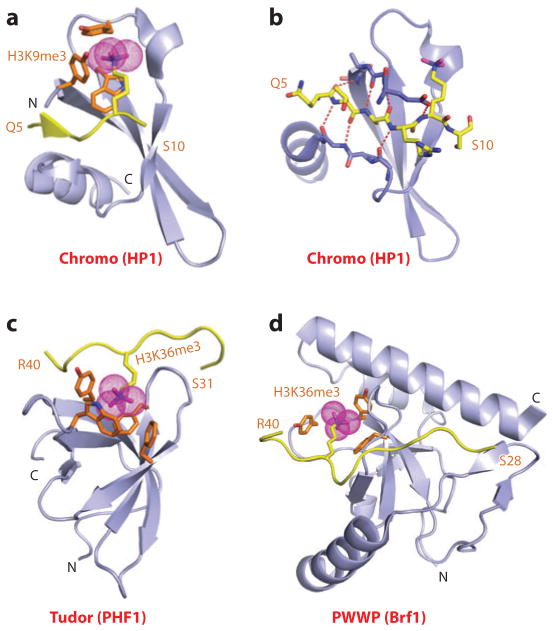
Figure 1.
Structures of single “Royal family” modules bound to methyl-lysine-containing histone peptides. (a) The 2.4-Å crystal structure of the complex of the HP1 chromodomain bound to the H3(1–15)K9me3 peptide, Protein Data Bank (PDB) reference 1KNE. The bound K9me3-containing H3 peptide can be traced from Gln5 to Ser10 (Q5 to S10). (b) Details of the antiparallel alignment of the β-strand of the bound H3K9me3-containing peptide sandwiched between the β-strands of the HP1 chromodomain, resulting in generation of a three-stranded antiparallel β-pleated sheet on formation of the complex. (c) The 1.85-Å crystal structure of the complex of the PHF1 Tudor domain bound to the H3(31–40)K36me3 peptide complex (PDB: 4HCZ). The bound K36me3-containing H3 peptide can be traced from Ser31 to Arg40 (S31 to R40). (d) The 1.5-Å crystal structure of the complex of the Brf1 PWWP domain bound to the H3(22–42)K36me3 peptide complex (PDB: 2X4W). The bound K36me3-containing H3 peptide can be traced from Ser28 to Arg40 (S28 to R40). Abbreviations: C, C terminus; N, N terminus.