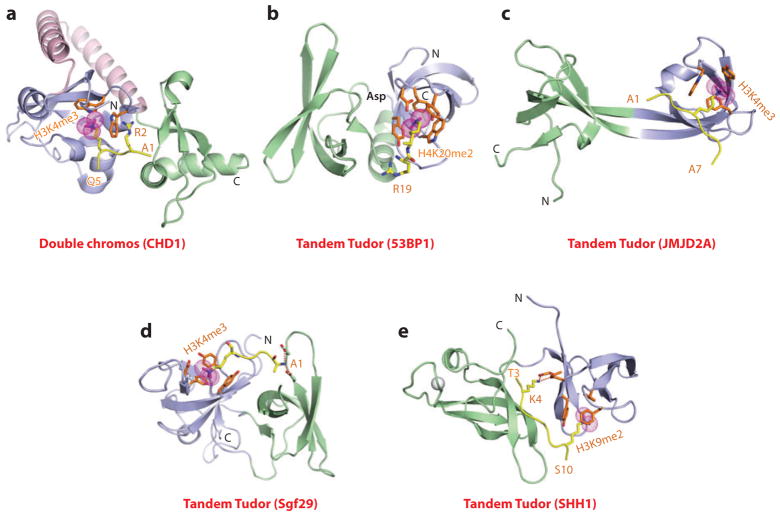
Figure 4.
Structures of tandem Royal family modules bound to methyl-lysine-containing histone peptides. (a) The 2.4-Å crystal structure of the complex of double chromo domains of human CHD1 proteins bound to the H3(1–19)K4me3 peptide, Protein Data Bank (PDB) reference 2B2W. Tudor domains 1 and 2 are shown (blue and green, respectively) with the connecting helix-turn-helix linker (pink). The bound K4me3-containing H3 peptide can be traced from Ala1 to Gln5 (A1 to Q5). (b) The 1.7-Å crystal structure of the complex of tandem Tudor domains of 53BP1 bound to the H4(15–24)K20me2 peptide (PDB: 2IG0). Tudor domains 1 and 2 are blue and green. The bound K20me2-containing H4 peptide can be traced for the Arg19-Lys20me2 (R19-K20me2) step. (c) The 2.1-Å crystal structure of the complex of tandem Tudor domains of JMJD2A bound to the H3(1–10)K4me3 peptide (PDB: 2GFA). Individual Tudor domains are blue and green. The bound K4me3-containing peptide can be traced from Ala1 to Ala7 (A1 to A7). (d) The 1.26-Å crystal structure of the complex of tandem Tudor domains of Sgf29 bound to the H3(1–11)K4me3 peptide (PDB: 3MEA). Tudor domains 1 and 2 are blue and green. The bound K4me3-containing peptide can be traced from Ala1 to Lys4me3 (A1 to K4me3). (e) The 2.7-Å crystal structure of the complex of tandem Tudor domains of the Arabidopsis thaliana SHH1 protein bound to the H3(1–15)K9me2 peptide (PDB: 4IUT). A bound zinc ion is shown (silver ball). Tudor domains 1 and 2 are blue and green. The bound K9me2-containing H3 peptide can be traced from Thr3 to Ser10 (T3 to S10). Abbreviations: C, C terminus; N, N terminus.