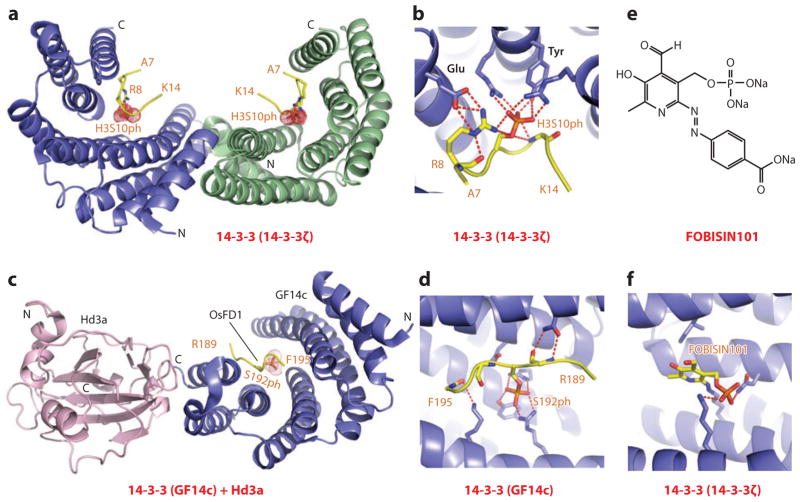
Figure 9.
Structures of 14-3-3 proteins bound to phosphoserine marks and inhibitors. (a) The 2.0-Å crystal structure of 14-3-3ζ bound to the H3(7–14)S10ph peptide, Protein Data Bank (PDB) reference 2C1N. The 14-3-3ζ protein in the complex adopts a symmetrical dimeric alignment, with individual monomers shown in blue and green. The bound peptide can be traced from Ala7 to Lys14 (A7 to K14). (b) Details of the alignment and hydrogen-bonding interactions involving the side chain of S10ph of the peptide in the H3(7–14)S10ph-14-3-3ζ complex. Also, note the pair of hydrogen bonds between the guanidinium group of Arg8 (R8) of the peptide and the carboxyl group of a Glu residue of the protein. (c) The 2.4-Å crystal structure of the ternary complex between Hd3a (pink), GF14c (blue), and the bound OsFD1(187–195)S192ph peptide (yellow) (PDB: 3AXY). The side chain can be traced from Arg189 to Phe195 (R189 to F195). (d) Details of the alignment and hydrogen-bonding interactions involving the side chain of phosphorylated Ser192 (S192ph) and the peptide in the ternary complex. (e) The chemical formula of FOBISIN101. (f) Details of interactions of the phosphate group of the cleaved pyridoxal-phosphate moiety of FOBISIN101 with 14-3-3ζ in the FOBISIN101-14-3-3ζ complex. Abbreviations: C, C terminus; N, N terminus.