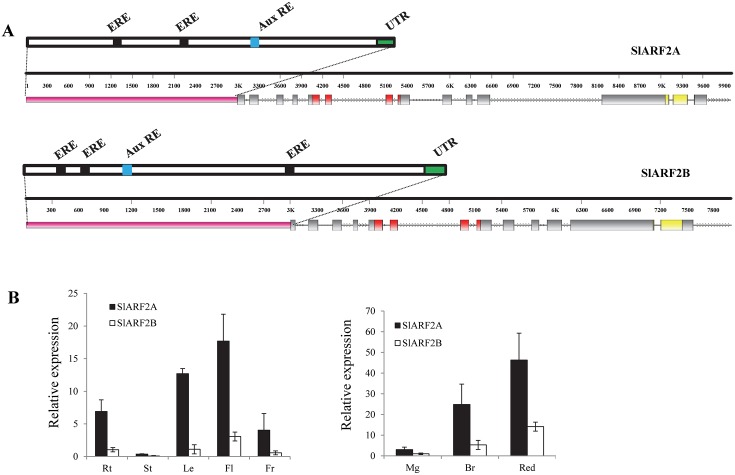
Fig 1. Structural features and expression patterns of tomato SlARF2A and SlARF2B genes.
(A) Genomic structure analysis of SlARF2A and SlARF2B genes were drawn using Fancy gene V1.4 software (http://bio.ieo.eu/fancygene/) and SlARF2A SlARF2B iTAG2.40 gene model data. The pink portion represents the promoter region; the strandlines represent intron parts; the gray boxes indicate exon parts; the yellow boxes region responsible for dimerization with Aux/IAA proteins (domain III and IV); the red boxes correspond to the DNA binding domain (DBD); ERE and AuxRE correspond to the ethylene and auxin responsive cis-elements. (B) Expression pattern of SlARF2A/2B monitored by quantitative real-time RT-PCR (qPCR) in total RNA samples extracted from root (Rt), stem (St), leaf (Le), flower (Fl), fruit (Fr), mature green fruit (MG), breaker fruit (Br) and red fruit (Re). Relative mRNA levels corresponding to SlARF2A/SlARF2B genes were normalized against actin in each RNA sample. The relative mRNA levels of SlARF2B in root and at mature green (MG) stage were used as reference (relative mRNA level 1). Error bars mean ±SD of three biological replicates.