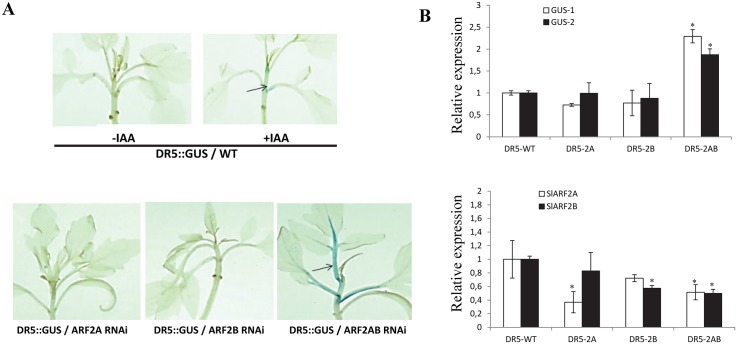
Fig 5. Impact of the down-regulation of SlARF2A and SlARF2B on auxin response assessed in planta following genetic crosses between DR5::GUS and SlARF2 down-regulated lines.
(A) Expression pattern of the GUS reporter gene under the control driven by the auxin-inducible DR5 promoter in wild type (WT) and SlARF2 down-regulated genetic background. Seedlings were treated with auxin (IAA 20 μM for 3 hours) or with a mock solution. Upper panel: in planta expression of the GUS reporter gene driven by DR5 in WT genetic background in the absence (left) or presence (right) of auxin treatment. Bottom panel: Expression of the GUS reporter gene driven by DR5 in ARF2A RNAi (left), ARF2B RNAi (middle) and ARF2AB RNAi (right) genetic background. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR expression analysis of GUS and SlARF2A/2B genes in WT and SlARF2A and SlARF2B-RNAi lines crossed with DR5::GUS lines. The relative mRNA levels of GUS-1/GUS-2 (Upper panel) and SlARF2A/2B (bottom panel) in wild type were standardized to 1.0, referring to the SlActin gene as internal control. Error bars mean ±SD of three biological replicates. *0.01 < p-value < 0.05. DR5-WT = DR5::GUS/WT; DR5-2A = DR5::GUS/ARF2A RNAi; DR5-2B = DR5::GUS/ARF2B RNAi; DR5-2AB = DR5::GUS/ARF2AB RNAi. GUS-1 and GUS-2 refer to the use of two distinct pairs of primers designed in two distinct regions of the GUS mRNA sequence.