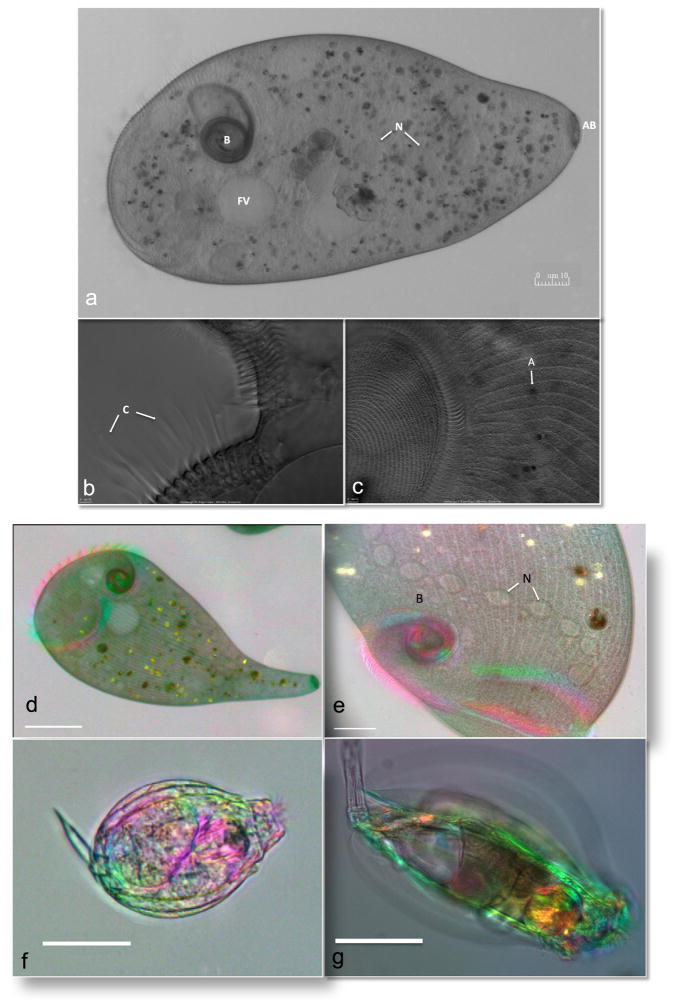
Fig. 2.
Imaging of Stentor species and rotifers. DIC imaging of the immobilized Stentor polymorphus with Olympus 20X (a) and 100X objective (b and c). (a) Stentor illustrating the buccal cavity (B), food vacuole (FV), nucleus (N), and attachment base (AB). (b) Close-up of the membranelles with the compound ciliary structures (C). (c) Oral field (left) and algal symbiont (A) are highighted. Birefringence imaging using a video-enhanced polychromatic polscope of Stentor coeruleus with 10X (d) and 40X (e) lens, showing the buccal cavity (B) and the moniliform macronucleus (N) which spans the length of the Stentor. Also see Videos 4, 5, and 6. The immobilized rotifers (f and g) found in pond water were imaged using the 10X lens. Also see Videos 7, 8 and 9. Scale bar is 10 μM.