Figure 5.
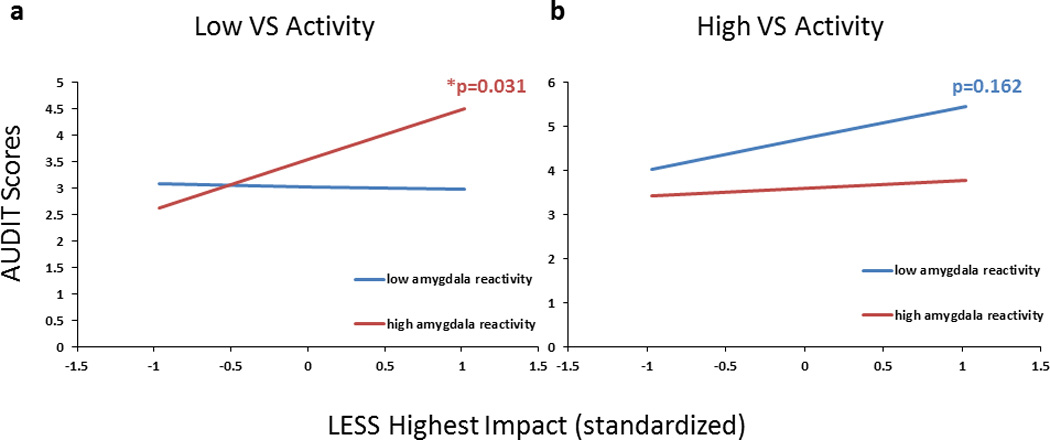
Amygdala and VS reactivity jointly moderated the relation between recent life stress and problem drinking three months following initial study completion. Slopes represent beta coefficient estimates reflecting the strength of the relation between LESS and AUDIT scores, measured at the three month follow-up assessment, as a function of varying levels of amygdala and VS activity assessed at baseline. High levels of stress were associated with larger increases in AUDIT scores for participants with a combination of low VS (-1SD) and high amygdala (+1SD) reactivity (a), but not for those with a combination of high VS and low amygdala reactivity (b). Simple slopes are adjusted for gender, age, race/ethnicity and CTQ.
