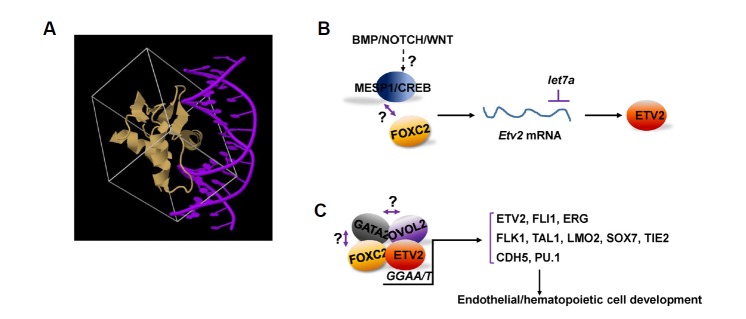
Fig. 1.
Regulation of the expression and function of ETV2. (A) A schematic structural diagram of the complex of the ETS domain of PU.1 in gold and DNA in purple (deposited on The RCSB PDB www.rcsb.org; DOI: 10.2210/pdb1pue/pdb) (Berman et al., 2000; Kodandapani et al., 1996). (B) In early embryos or differentiating mouse ES cells, BMP/NOTCH/WNT pathways act upstream of ETV2 expression. During this process, transcriptional activation of Etv2 is induced by at least MESP1, CREB and FOXC2. let7a functions to inhibit ETV2 protein synthesis. It is of note that the relationship between BMP/NOTCH/WNT pathways to MESP, CREB and FOXC2 is not known. Also, whether the three transcription factors interact each other in regulating Etv2 gene expression remain elucidated. (C) ETV2 can bind and activate promoters/enhancers of genes critical for endothelial and hematopoietic cell development. OVOL2, FOXC2, GATA2 are reported to interact with ETV2 in mediating these regulation. Whether the three transcription factors can form a transcriptionally active complex remains determined.