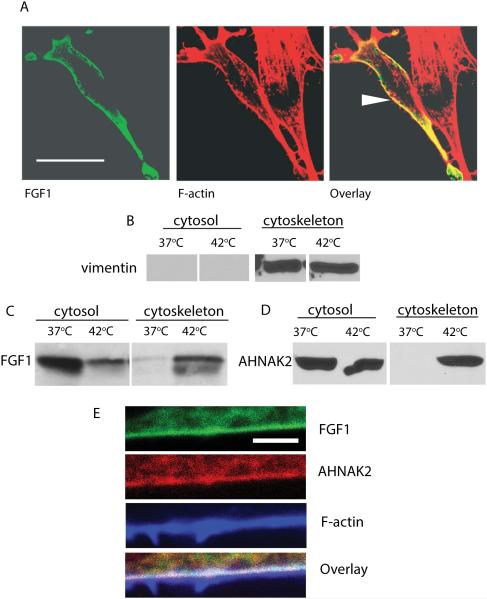
Figure 4. Heat shock induces the association of FGF1 and ctAHNAK2 with the cytoskeleton.
(A) NIH 3T3 cells transfected with FGF1:HA were subjected to a 90 min incubation at 42°C. FGF1 was detected by using FITC-labeled anti-HA antibodies (green) and F actin by using CY3-labeled phalloidin (red). Cells were studied via a confocal microscope. Arrow indicates FGF1 and F-actin colocalization at the cell periphery. Scale bar – 32 μm. (B,C) NIH 3T3 cells transfected with FGF1:HA were incubated for 90 min at 37°C or 42°C. Cytosolic and cytoskeletal fractions were prepared by utilizing the Qiagen kit, resolved by SDS PAGE and immunoblotted with vimentin antibodies (cytoskeleton marker) (B) or FGF1 antibodies (C). (D) NIH 3T3 cells adenovirally transduced with ctAHNAK2:V5 were treated and fractionated similar to (B), ctAHNAK2 was detected by using anti-V5 antibodies. E. Co-localization of FGF1, AHNAK2 and F-actin at the periphery of a stressed cell. NIH 3T3 cells were co-transduced with FGF1:HA and ctAHNAK2:V5, and heat shocked. Fixed cells were immunofluorescently stained with FITC-labeled anti-HA antibodies (green), CY3-labeled anti-V5 antibodies (red) and Alexa 633-labeled phalloidin (blue), and studied via a confocal microscope. Scale bar – 2 μm.